Aspergillus galactomannan enzyme immunoassay and quantitative PCR for diagnosis of invasive aspergillosis with bronchoalveolar lavage fluid
- PMID: 15583275
- PMCID: PMC535238
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.42.12.5517-5522.2004
Aspergillus galactomannan enzyme immunoassay and quantitative PCR for diagnosis of invasive aspergillosis with bronchoalveolar lavage fluid
Abstract
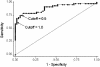
Invasive pulmonary aspergillosis (IPA) is frequent and often fatal in hematopoietic stem cell transplant patients. Diagnosis requires microbiological or histopathologic demonstration of the organism in tissues; however, cultivation of Aspergillus species from respiratory secretions has low diagnostic sensitivity. Assays to detect Aspergillus antigen or DNA in bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) fluid could facilitate earlier diagnosis, thereby guiding optimal therapy and obviating the need for additional costly and potentially morbid diagnostic evaluation. We evaluated the performance of a galactomannan enzyme immunoassay (GM EIA; Bio-Rad) by using a range of index cutoffs to define positivity and a quantitative PCR (qPCR) assay for the detection of Aspergillus species from BAL samples of patients with proven and probable IPA (case patients; n = 49) and without IPA (control patients; n = 50). The sensitivity of the GM EIA was 61% with an index cutoff of 1.0 and 76% with an index cutoff of 0.5; the corresponding specificities were 98 and 94%, respectively. The sensitivity and specificity of qPCR assay were 67 and 100%, respectively. The sensitivity with 22 culture-negative BAL specimens from patients with IPA was 41% for GM EIA with an index cutoff of 1.0, 59% for GM EIA with an index cutoff of 0.5, and 36% for qPCR assay. GM EIA indices and DNA quantities corresponded to BAL fungal burdens, with culture-positive samples having larger amounts of antigen and DNA compared to culture-negative samples. GM EIA and qPCR assay add to the sensitivity of BAL for diagnosing IPA in high-risk patients, with excellent specificity. Adjunctive use of these tests may reduce dependence on invasive diagnostic procedures.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Characterization and comparison of galactomannan enzyme immunoassay and quantitative real-time PCR assay for detection of Aspergillus fumigatus in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid from experimental invasive pulmonary aspergillosis.J Clin Microbiol. 2006 Jul;44(7):2475-80. doi: 10.1128/JCM.02693-05. J Clin Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 16825367 Free PMC article.
-
[Evaluation of risk factors for invasive pulmonary aspergillosis and detection of diagnostic values of galactomannan and PCR methods in bronchoalveolar lavage samples from non-neutropenic intensive care unit patients].Mikrobiyol Bul. 2015 Oct;49(4):565-75. doi: 10.5578/mb.9906. Mikrobiyol Bul. 2015. PMID: 26649414 Turkish.
-
Clinical utility of Aspergillus galactomannan and PCR in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid for the diagnosis of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in patients with haematological malignancies.Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2014 Jul;79(3):322-7. doi: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2014.03.020. Epub 2014 Mar 29. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2014. PMID: 24768294
-
Utility of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid galactomannan alone or in combination with PCR for the diagnosis of invasive aspergillosis in adult hematology patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Crit Rev Microbiol. 2015 Feb;41(1):124-34. doi: 10.3109/1040841X.2013.804033. Epub 2013 Jun 25. Crit Rev Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 23799871
-
Aspergillus polymerase chain reaction (PCR) diagnosis.Med Mycol. 2005 May;43 Suppl 1:S139-45. doi: 10.1080/13693780500051596. Med Mycol. 2005. PMID: 16110806 Review.
Cited by
-
Diagnosis of Invasive Fungal Diseases in Hematological Malignancies: A Critical Review of Evidence and Turkish Expert Opinion (TEO-2).Turk J Haematol. 2014 Dec 5;31(4):342-56. doi: 10.4274/tjh.2014.0218. Turk J Haematol. 2014. PMID: 25541650 Free PMC article.
-
Plasmalyte as a cause of false-positive results for Aspergillus galactomannan in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid.J Clin Microbiol. 2007 Feb;45(2):676-7. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01940-06. Epub 2006 Dec 13. J Clin Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17166959 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Murine model for Fusarium oxysporum invasive fusariosis reveals organ-specific structures for dissemination and long-term persistence.PLoS One. 2014 Feb 27;9(2):e89920. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0089920. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24587124 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Two Commercial Real-Time PCR Kits for Aspergillus DNA Detection in Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid in Patients with Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis.J Mol Diagn. 2018 May;20(3):298-306. doi: 10.1016/j.jmoldx.2017.12.005. Epub 2018 Feb 19. J Mol Diagn. 2018. PMID: 29471112 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic Accuracy of Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid Galactomannan for Invasive Aspergillosis.Biomed Res Int. 2020 Nov 30;2020:5434589. doi: 10.1155/2020/5434589. eCollection 2020. Biomed Res Int. 2020. PMID: 33335924 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ascioglu, A., J. Rex, B. DePauw, J. E. Bennett, J. Bille, F. Crokaert, D. W. Denning, J. P. Donnelly, J. E. Edwards, Z. Erjavec, D. Fiere, O. Lortholary, J. Maertens, J. F. Meis, T. F. Patterson, J. Ritter, D. Selleslag, P. M. Shah, D. A. Stevens, and T. J. Walsh. 2002. Defining opportunistic invasive fungal infections in immunocompromised patients with cancer and hematopoietic stem cell transplants: an international consensus. Clin. Infect. Dis. 34:7-14. - PubMed
-
- Becker, M. J., E. J. Lugtenburg, J. J. Cornelissen, C. Van Der Schee, H. C. Hoogsteden, and S. De Marie. 2003. Galactomannan detection in computerized tomography-based broncho-alveolar lavage fluid and serum in haematological patients at risk for invasive pulmonary aspergillosis. Br. J. Haematol. 121:448-457. - PubMed
-
- Berenguer, J., M. C. Allende, J. W. Lee, K. Garrett, C. Lyman, N. M. Ali, J. Bacher, P. A. Pizzo, and T. J. Walsh. 1995. Pathogenesis of pulmonary aspergillosis. Granulocytopenia versus cyclosporine and methylprednisolone-induced immunosuppression. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 152:1079-1086. - PubMed
-
- Buchheidt, D., C. Baust, H. Skladny, J. Ritter, T. Suedhoff, M. Baldus, W. Seifarth, C. Leib-Moesch, and R. Hehlmann. 2001. Detection of Aspergillus species in blood and bronchoalveolar lavage samples from immunocompromised patients by means of 2-step polymerase chain reaction: clinical results. Clin. Infect. Dis. 33:428-435. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical