Phylogenetic analysis and PCR-restriction fragment length polymorphism identification of Campylobacter species based on partial groEL gene sequences
- PMID: 15583306
- PMCID: PMC535295
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.42.12.5731-5738.2004
Phylogenetic analysis and PCR-restriction fragment length polymorphism identification of Campylobacter species based on partial groEL gene sequences
Abstract
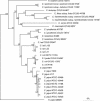
The phylogeny of 12 Campylobacter species and reference strains of Arcobacter butzleri and Helicobacter pylori was studied based on partial 593-bp groEL gene sequences. The topology of the phylogenetic neighbor-joining tree based on the groEL gene was similar to that of the tree based on the 16S rRNA gene. However, groEL was found to provide a better resolution for Campylobacter species, with lower interspecies sequence similarities (range, 65 to 94%) compared with those for the 16S rRNA gene (range, 90 to 99%) and high intraspecies sequence similarities (range, 95 to 100%; average, 99%). A new universal reverse primer that amplifies a 517-bp fragment of the groEL gene was developed and used for PCR-restriction fragment length polymorphism (PCR-RFLP) analysis of 68 strains representing 11 Campylobacter species as well as reference strains of A. butzlerii and H. pylori. Digestion with the AluI enzyme discriminated all Campylobacter species included in the study but showed more intraspecies diversity than digestion with the ApoI enzyme. A hippurate-negative variant of Campylobacter jejuni with a high level of groEL sequence similarity to both C. jejuni (96%) and C. coli (94%) gave a unique AluI profile and an ApoI profile identical to those of other C. jejuni strains. In conclusion, groEL gene sequencing and PCR-RFLP analysis are recommended as valuable tools for the identification of Campylobacter species.
Figures


References
-
- Alderton, M. R., V. Korolik, P. J. Coloe, F. E. Dewhrist, and B. J. Paster. 1995. Campylobacter hyoilei sp. nov., associated with porcine proliferative enteritis. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 45:61-66. - PubMed
-
- Cardarelli-Leite, P., K. Blom, C. M. Patton, M. A. Nicholson, A. G. Steigerwalt, S. B. Hunter, D. J. Brenner, T. J. Barrett, and B. Swaminathan. 1996. Rapid identification of Campylobacter species by restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis of a PCR-amplified fragment of the gene coding for 16S rRNA. J. Clin. Microbiol. 34:62-67. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Corry, J. E. L., D. E. Post, P. Collin, and M. J. Laisney. 1995. Culture media for the isolation of campylobacters. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 26:43-76. - PubMed
-
- Duim, B., P. A. R. Vandamme, A. Rigter, S. Laevens, J. R. Dijkstra, and J. A. Wagenaar. 2001. Differentiation of Campylobacter species by AFLP fingerprinting. Microbiology 147:2729-2737. - PubMed
-
- Euzéby, J. P. 1997. List of bacterial names with standing in nomenclature: a folder available on the Internet (URL: http://www.bacterio.cict.fr/). Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 47:590-592. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

