Possible involvement of CS-ACS1 and ethylene in auxin-induced peg formation of cucumber seedlings
- PMID: 15585540
- PMCID: PMC4246792
- DOI: 10.1093/aob/mci045
Possible involvement of CS-ACS1 and ethylene in auxin-induced peg formation of cucumber seedlings
Abstract
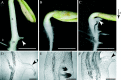
Background and aims: Cucumber (Cucumis sativus) seedlings develop a peg on the concave side of the gravitropically bending transition zone between the hypocotyl and the root after seed germination. Peg initiation occurs in response to auxin when its levels in the concave side of the transition zone exceed a particular threshold through the graviresponse. Ethylene also plays an important role in peg formation, but its relationship to auxin in this event is not understood. Here, the role ethylene plays in auxin-induced peg formation is studied.
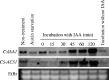
Methods: Peg formation of cucumber seedlings exposed to ethylene at different stages of growth or during exogenous auxin treatment was observed. In addition, ethylene evolution from the concave and convex sides of the transition zone was compared and their transcription of CS-ACS (1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid synthase) genes was analysed by RT-PCR and in situ hybridization.
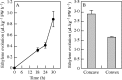
Key results: Seedlings treated with ethylene after peg initiation produced an enlarged peg, whereas ethylene treatment before peg initiation inhibited peg formation. Ethylene also promoted the development of the peg in the auxin-treated seedlings. Furthermore, the concave side of the transition zone at peg initiation produced more ethylene and CS-ACS1 mRNA than the convex side.
Conclusions: Since CS-ACS1 is an auxin-inducible gene, the greater abundance of auxin in the concave side of the transition zone causes peg initiation and increases CS-ACS1-mediated ethylene biosynthesis, which then facilitates peg development.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Differential accumulation of the mRNA of the auxin-repressed gene CsGRP1 and the auxin-induced peg formation during gravimorphogenesis of cucumber seedlings.Planta. 2006 Dec;225(1):13-22. doi: 10.1007/s00425-006-0324-y. Epub 2006 Jun 14. Planta. 2006. PMID: 16773375
-
Gravity-induced modification of auxin transport and distribution for peg formation in cucumber seedlings: possible roles for CS-AUX1 and CS-PIN1.Planta. 2003 Nov;218(1):15-26. doi: 10.1007/s00425-003-1072-x. Epub 2003 Aug 7. Planta. 2003. PMID: 12905024
-
Control of gravimorphogenesis by auxin: accumulation pattern of CS-IAA1 mRNA in cucumber seedlings grown in space and on the ground.Planta. 2000 Sep;211(4):493-501. doi: 10.1007/s004250000321. Planta. 2000. PMID: 11030548
-
On hormonal regulation of the dynamic apical hook development.New Phytol. 2019 May;222(3):1230-1234. doi: 10.1111/nph.15626. Epub 2018 Dec 31. New Phytol. 2019. PMID: 30537131 Review.
-
Auxin-regulated gene expression in plants.Biotechnology. 1989;12:229-43. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-409-90068-2.50017-4. Biotechnology. 1989. PMID: 2653477 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Analysis of expression profile of selected genes expressed during auxin-induced somatic embryogenesis in leaf base system of wheat (Triticum aestivum) and their possible interactions.Plant Mol Biol. 2007 Nov;65(5):677-92. doi: 10.1007/s11103-007-9234-z. Epub 2007 Sep 12. Plant Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17849219
-
Gravistimulation changes the accumulation pattern of the CsPIN1 auxin efflux facilitator in the endodermis of the transition zone in cucumber seedlings.Plant Physiol. 2012 Jan;158(1):239-51. doi: 10.1104/pp.111.188615. Epub 2011 Nov 7. Plant Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22065422 Free PMC article.
-
P-chlorophenoxyisobutyric acid impairs auxin response for gravity-regulated peg formation in cucumber (Cucumis sativus) seedlings.J Plant Res. 2008 Jan;121(1):107-14. doi: 10.1007/s10265-007-0121-0. Epub 2007 Nov 7. J Plant Res. 2008. PMID: 17987258
-
Differential accumulation of the mRNA of the auxin-repressed gene CsGRP1 and the auxin-induced peg formation during gravimorphogenesis of cucumber seedlings.Planta. 2006 Dec;225(1):13-22. doi: 10.1007/s00425-006-0324-y. Epub 2006 Jun 14. Planta. 2006. PMID: 16773375
References
-
- Fujii N, Kamada M, Yamasaki S, Takahashi H. 2000. Differential accumulation of Aux/IAA mRNA during seedling development and gravity response in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.). Plant Molecular Biology 42: 731–740. - PubMed
-
- Kamachi S, Sekimoto H, Kondo N, Sakai S. 1997. Cloning of a cDNA for a 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate synthase that is expressed during development of female flowers at the apices of Cucumis sativus L. Plant and Cell Physiology 38: 1197–1206. - PubMed
-
- Kamada M, Fujii N, Aizawa S, Kamigaichi S, Mukai C, Shimazu T, Takahashi H. 2000. Control of gravimorphogenesis by auxin: accumulation pattern of CS-IAA1 mRNA in cucumber seedlings grown in space and on the ground. Planta 211: 493–501. - PubMed

