Mutations in the JARID1C gene, which is involved in transcriptional regulation and chromatin remodeling, cause X-linked mental retardation
- PMID: 15586325
- PMCID: PMC1196368
- DOI: 10.1086/427563
Mutations in the JARID1C gene, which is involved in transcriptional regulation and chromatin remodeling, cause X-linked mental retardation
Abstract
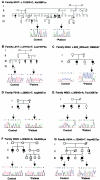
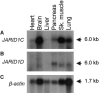
In families with nonsyndromic X-linked mental retardation (NS-XLMR), >30% of mutations seem to cluster on proximal Xp and in the pericentric region. In a systematic screen of brain-expressed genes from this region in 210 families with XLMR, we identified seven different mutations in JARID1C, including one frameshift mutation and two nonsense mutations that introduce premature stop codons, as well as four missense mutations that alter evolutionarily conserved amino acids. In two of these families, expression studies revealed the almost complete absence of the mutated JARID1C transcript, suggesting that the phenotype in these families results from functional loss of the JARID1C protein. JARID1C (Jumonji AT-rich interactive domain 1C), formerly known as "SMCX," is highly similar to the Y-chromosomal gene JARID1D/SMCY, which encodes the H-Y antigen. The JARID1C protein belongs to the highly conserved ARID protein family. It contains several DNA-binding motifs that link it to transcriptional regulation and chromatin remodeling, processes that are defective in various other forms of mental retardation. Our results suggest that JARID1C mutations are a relatively common cause of XLMR and that this gene might play an important role in human brain function.
Figures

References
Electronic-Database Information
-
- Conserved Domain Database, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/cdd/cdd.shtml
-
- GenBank, http://www.ncbi.nih.gov/Genbank/ (for JARID1C [accession number L25270], JARID1C [accession number P41229], JARID1D [accession number NM_004653], JARID1D [accession number NP_004644], JARID1A [accession number NP_005047], JARID1B [accession number NP_006609], Jarid1c [accession number NP_038696], Lid [accession number NP_723140], and ZK593.4 [accession number CAA93426])
-
- Human Genome Browser Gateway, http://genome.cse.ucsc.edu/cgi-bin/hgGateway?db=hg10
-
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/Omim/ (for FMR2, OPHN1, PAK3,GDI1, IL1RAPL1, TM4SF2, ARHGEF6, MECP2, FACL4, ARX, ELK1, ALAS2, PQBP1, FTSJ1, JARID1C, JARID1D/SMCY, USP9X/Y, RPS4X/Y, UTX/Y, and SLC6A8)
References
-
- Agulnik AI, Mitchell MJ, Mattei MG, Borsani G, Avner PA, Lerner JL, Bishop CE (1994) A novel X gene with a widely transcribed Y-linked homologue escapes X-inactivation in mouse and human. Hum Mol Genet 3:879–884 - PubMed
-
- Asselta R, Duga S, Spena S, Santagostino E, Peyvandi F, Piseddu G, Targhetta R, Malcovati M, Mannucci PM, Tenchini ML (2001) Congenital afibrinogenemia: mutations leading to premature termination codons in fibrinogen A α-chain gene are not associated with the decay of the mutant mRNAs. Blood 98:3685–369210.1182/blood.V98.13.3685 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bienvenu T, Poirer K, Friocourt G, Bahi N, Beaumont D, Fauchereau F, Ben Jeema L, Zemni R, Vinet MC, Francis F, Couvert P, Gomot M, Moraine C, Van Bokhoven H, Kalscheuer V, Frints S, Gécz F, Ohzaki K, Chaabouni H, Fryns JP, Desportes V, Beldjord C, Chelly J (2002) ARX, a novel Prd-class-homeobox gene highly expressed in the telencephalon, is mutated in X-linked mental retardation. Hum Mol Genet 11:981–99110.1093/hmg/11.8.981 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chelly J, Hamel BCJ (2003) Genetics of X-linked mental retardation. In: Fisch GS (ed) Genetics and genomics of neurobehavioral disorders. Humana Press, Totowa, NJ, pp 263–287
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

