K+ channel types targeted by synthetic OSK1, a toxin from Orthochirus scrobiculosus scorpion venom
- PMID: 15588251
- PMCID: PMC1134677
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20041379
K+ channel types targeted by synthetic OSK1, a toxin from Orthochirus scrobiculosus scorpion venom
Abstract
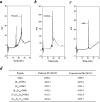
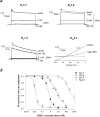
OSK1 (alpha-KTx3.7) is a 38-residue toxin cross-linked by three disulphide bridges that was initially isolated from the venom of the Asian scorpion Orthochirus scrobiculosus. OSK1 and several structural analogues were produced by solid-phase chemical synthesis, and were tested for lethality in mice and for their efficacy in blocking a series of 14 voltage-gated and Ca2+-activated K+ channels in vitro. In the present paper, we report that OSK1 is lethal in mice by intracerebroventricular injection, with a LD50 (50% lethal dose) value of 2 microg/kg. OSK1 blocks K(v)1.1, K(v)1.2, K(v)1.3 channels potently and K(Ca)3.1 channel moderately, with IC50 values of 0.6, 5.4, 0.014 and 225 nM respectively. Structural analogues of OSK1, in which we mutated positions 16 (Glu16-->Lys) and/or 20 (Lys20-->Asp) to amino acid residues that are conserved in all other members of the alpha-KTx3 toxin family except OSK1, were also produced and tested. Among the OSK1 analogues, [K16,D20]-OSK1 (OSK1 with Glu16-->Lys and Lys20-->Asp mutations) shows an increased potency on K(v)1.3 channel, with an IC50 value of 0.003 nM, without loss of activity on K(Ca)3.1 channel. These data suggest that OSK1 or [K16,D20]-OSK1 could serve as leads for the design and production of new immunosuppressive drugs.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Cobatoxin 1 from Centruroides noxius scorpion venom: chemical synthesis, three-dimensional structure in solution, pharmacology and docking on K+ channels.Biochem J. 2004 Jan 1;377(Pt 1):37-49. doi: 10.1042/BJ20030977. Biochem J. 2004. PMID: 14498829 Free PMC article.
-
The 'functional' dyad of scorpion toxin Pi1 is not itself a prerequisite for toxin binding to the voltage-gated Kv1.2 potassium channels.Biochem J. 2004 Jan 1;377(Pt 1):25-36. doi: 10.1042/BJ20030115. Biochem J. 2004. PMID: 12962541 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological profiling of Orthochirus scrobiculosus toxin 1 analogs with a trimmed N-terminal domain.Mol Pharmacol. 2006 Jan;69(1):354-62. doi: 10.1124/mol.105.017210. Epub 2005 Oct 18. Mol Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16234482
-
Potassium channel blockers from the venom of the Brazilian scorpion Tityus serrulatus ().Toxicon. 2016 Sep 1;119:253-65. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2016.06.016. Epub 2016 Jun 25. Toxicon. 2016. PMID: 27349167 Review.
-
Diverse Structural Features of Potassium Channels Characterized by Scorpion Toxins as Molecular Probes.Molecules. 2019 May 29;24(11):2045. doi: 10.3390/molecules24112045. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31146335 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
From Animal Poisons and Venoms to Medicines: Achievements, Challenges and Perspectives in Drug Discovery.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Jul 24;11:1132. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.01132. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32848750 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Scorpion Potassium Channel-blocking Defensin Highlights a Functional Link with Neurotoxin.J Biol Chem. 2016 Mar 25;291(13):7097-106. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.680611. Epub 2016 Jan 27. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 26817841 Free PMC article.
-
Structural basis of the selective block of Kv1.2 by maurotoxin from computer simulations.PLoS One. 2012;7(10):e47253. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0047253. Epub 2012 Oct 10. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23071772 Free PMC article.
-
Scorpion toxins specific for potassium (K+) channels: a historical overview of peptide bioengineering.Toxins (Basel). 2012 Nov 1;4(11):1082-119. doi: 10.3390/toxins4111082. Toxins (Basel). 2012. PMID: 23202307 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular and cellular basis of small--and intermediate-conductance, calcium-activated potassium channel function in the brain.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2008 Oct;65(20):3196-217. doi: 10.1007/s00018-008-8216-x. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2008. PMID: 18597044 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jaravine V. A., Nolde D. E., Reibarkh M. J., Korolkova Y. V., Kozlov S. A., Pluzhnikov K. A., Grishin E. V., Arseniev A. S. Three-dimensional structure of toxin from Orthochirus scrobiculosus scorpion venom. Biochemistry. 1997;36:1223–1232. - PubMed
-
- Bontems F., Roumestand C., Gilquin B., Ménez A., Toma F. Refined structure of charybdotoxin: common motifs in scorpion toxins and insect defensins. Science. 1991;254:1521–1523. - PubMed
-
- Aiyar J., Withka J. M., Rizzi J. P., Singleton D. H., Andrews G. C., Lin W., Boyd J., Hanson D. C., Simon M., Dethlefs B., et al. Topology of the pore-region of a K+ channel revealed by the NMR-derived structures of scorpion toxins. Neuron. 1995;15:1169–1181. - PubMed
-
- Garcia M. L., Garcia-Calvo M., Hidalgo P., Lee A., MacKinnon R. Purification and characterization of three inhibitors of voltage-dependent K+ channels from Leiurus quinquestriatus var. hebraeus venom. Biochemistry. 1994;33:6834–6839. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

