Drosophila Wee1 kinase regulates Cdk1 and mitotic entry during embryogenesis
- PMID: 15589158
- PMCID: PMC3242732
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2004.11.050
Drosophila Wee1 kinase regulates Cdk1 and mitotic entry during embryogenesis
Abstract
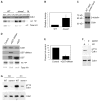
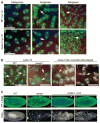
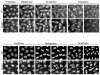
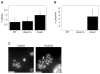
Cyclin-dependent kinases (Cdks) are the central regulators of the cell division cycle. Inhibitors of Cdks ensure proper coordination of cell cycle events and help regulate cell proliferation in the context of tissues and organs. Wee1 homologs phosphorylate a conserved tyrosine to inhibit the mitotic cyclin-dependent kinase Cdk1. Loss of Wee1 function in fission or budding yeast causes premature entry into mitosis. The importance of metazoan Wee1 homologs for timing mitosis, however, has been demonstrated only in Xenopus egg extracts and via ectopic Cdk1 activation . Here, we report that Drosophila Wee1 (dWee1) regulates Cdk1 via phosphorylation of tyrosine 15 and times mitotic entry during the cortical nuclear cycles of syncytial blastoderm embryos, which lack gap phases. Loss of maternal dwee1 leads to premature entry into mitosis, mitotic spindle defects, chromosome condensation problems, and a Chk2-dependent block of subsequent development, and then embryonic lethality. These findings modify previous models about cell cycle regulation in syncytial embryos and demonstrate that Wee1 kinases can regulate mitotic entry in vivo during metazoan development even in cycles that lack a G2 phase.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Drosophila Wee1 interacts with members of the gammaTURC and is required for proper mitotic-spindle morphogenesis and positioning.Curr Biol. 2005 Sep 6;15(17):1525-34. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2005.07.031. Curr Biol. 2005. PMID: 16139207 Free PMC article.
-
Drosophila Wee1 kinase rescues fission yeast from mitotic catastrophe and phosphorylates Drosophila Cdc2 in vitro.Mol Biol Cell. 1995 Oct;6(10):1333-47. doi: 10.1091/mbc.6.10.1333. Mol Biol Cell. 1995. PMID: 8573790 Free PMC article.
-
Tyrosines in the kinesin-5 head domain are necessary for phosphorylation by Wee1 and for mitotic spindle integrity.Curr Biol. 2009 Oct 13;19(19):1670-6. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2009.08.013. Epub 2009 Oct 1. Curr Biol. 2009. PMID: 19800237 Free PMC article.
-
WEE1 kinase limits CDK activities to safeguard DNA replication and mitotic entry.Mutat Res. 2020 Jan-Apr;819-820:111694. doi: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2020.111694. Epub 2020 Feb 25. Mutat Res. 2020. PMID: 32120135 Review.
-
Dynamic changes in nuclear architecture during mitosis: on the role of protein phosphorylation in spindle assembly and chromosome segregation.Exp Cell Res. 1996 Dec 15;229(2):174-80. doi: 10.1006/excr.1996.0356. Exp Cell Res. 1996. PMID: 8986594 Review.
Cited by
-
Local circadian clock gates cell cycle progression of transient amplifying cells during regenerative hair cycling.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Jun 4;110(23):E2106-15. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1215935110. Epub 2013 May 20. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 23690597 Free PMC article.
-
The FHA domain determines Drosophila Chk2/Mnk localization to key mitotic structures and is essential for early embryonic DNA damage responses.Mol Biol Cell. 2015 May 15;26(10):1811-28. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E14-07-1238. Epub 2015 Mar 25. Mol Biol Cell. 2015. PMID: 25808488 Free PMC article.
-
Drosophila Xpd regulates Cdk7 localization, mitotic kinase activity, spindle dynamics, and chromosome segregation.PLoS Genet. 2010 Mar 12;6(3):e1000876. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000876. PLoS Genet. 2010. PMID: 20300654 Free PMC article.
-
Drosophila Wee1 interacts with members of the gammaTURC and is required for proper mitotic-spindle morphogenesis and positioning.Curr Biol. 2005 Sep 6;15(17):1525-34. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2005.07.031. Curr Biol. 2005. PMID: 16139207 Free PMC article.
-
Death-effector domain-containing protein DEDD is an inhibitor of mitotic Cdk1/cyclin B1.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Feb 13;104(7):2289-94. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0611167104. Epub 2007 Feb 5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 17283331 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kellogg DR. Wee1-dependent mechanisms required for coordination of cell growth and cell division. J Cell Sci. 2003;116:4883–4890. - PubMed
-
- Nurse P. Genetic control of cell size at cell division in yeast. Nature. 1975;256:547–551. - PubMed
-
- Harvey SL, Kellogg DR. Conservation of mechanisms controlling entry into mitosis: Budding yeast wee1 delays entry into mitosis and is required for cell size control. Curr Biol. 2003;13:264–275. - PubMed
-
- Heald R, McLoughlin M, McKeon F. Human wee1 maintains mitotic timing by protecting the nucleus from cytoplasmically activated Cdc2 kinase. Cell. 1993;74:463–474. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

