Executive dysfunction in cocaine addiction: evidence for discordant frontal, cingulate, and cerebellar activity
- PMID: 15590917
- PMCID: PMC6730277
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3321-04.2004
Executive dysfunction in cocaine addiction: evidence for discordant frontal, cingulate, and cerebellar activity
Abstract
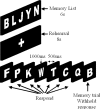
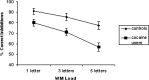
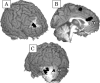
Using a GO-NOGO response inhibition task in which working memory (WM) demands can be varied, we demonstrate that the compromised abilities of cocaine users to exert control over strong prepotent urges are associated with reduced activity in anterior cingulate and right prefrontal cortices, two regions thought to be critical for implementing cognitive control. Furthermore, unlike drug-naive controls, and opposite to the anterior cingulate pattern, cocaine users showed an over-reliance on the left cerebellum, a compensatory pattern previously seen in alcohol addiction. The results indicate that cocaine users find it difficult to inhibit their own actions, particularly when WM demands, which have been shown previously to increase during cue-induced craving for the drug, are increased. The results reveal a neuroanatomical basis for this dysexecutive component to addiction, supporting the suggested importance cognitive functions may play in prolonging abuse or predisposing users toward relapse.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cingulate hypoactivity in cocaine users during a GO-NOGO task as revealed by event-related functional magnetic resonance imaging.J Neurosci. 2003 Aug 27;23(21):7839-43. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-21-07839.2003. J Neurosci. 2003. PMID: 12944513 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of task difficulty on motor performance and frontal-striatal connectivity in cocaine users.Drug Alcohol Depend. 2017 Apr 1;173:178-184. doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2016.12.008. Epub 2017 Jan 21. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2017. PMID: 28260681 Free PMC article.
-
The neurobiology of cognitive control in successful cocaine abstinence.Drug Alcohol Depend. 2012 Feb 1;121(1-2):45-53. doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2011.08.007. Epub 2011 Aug 31. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2012. PMID: 21885214 Free PMC article.
-
Drug addiction and its underlying neurobiological basis: neuroimaging evidence for the involvement of the frontal cortex.Am J Psychiatry. 2002 Oct;159(10):1642-52. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.159.10.1642. Am J Psychiatry. 2002. PMID: 12359667 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Structural and functional neuroanatomy of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)].Encephale. 2009 Apr;35(2):107-14. doi: 10.1016/j.encep.2008.01.005. Epub 2008 Jul 7. Encephale. 2009. PMID: 19393378 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Dopaminergic involvement during mental fatigue in health and cocaine addiction.Transl Psychiatry. 2012 Oct 23;2(10):e176. doi: 10.1038/tp.2012.110. Transl Psychiatry. 2012. PMID: 23092980 Free PMC article.
-
PET studies in nonhuman primate models of cocaine abuse: translational research related to vulnerability and neuroadaptations.Neuropharmacology. 2014 Sep;84:138-51. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.02.004. Epub 2013 Feb 28. Neuropharmacology. 2014. PMID: 23458573 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adolescents' fMRI activation to a response inhibition task predicts future substance use.Addict Behav. 2013 Jan;38(1):1435-41. doi: 10.1016/j.addbeh.2012.07.012. Epub 2012 Jul 28. Addict Behav. 2013. PMID: 23006248 Free PMC article.
-
Power spectrum scale invariance as a neural marker of cocaine misuse and altered cognitive control.Neuroimage Clin. 2016 Mar 4;11:349-356. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2016.03.004. eCollection 2016. Neuroimage Clin. 2016. PMID: 27294029 Free PMC article.
-
Attenuated Neural Processing of Risk in Young Adults at Risk for Stimulant Dependence.PLoS One. 2015 Jun 15;10(6):e0127010. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0127010. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26076493 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ardila A, Rosselli M, Strumwasser S (1991) Neuropsychological deficits in chronic cocaine abusers. Int J Neurosci 57: 73-79. - PubMed
-
- Aron AR, Robbins TW, Poldrack RA (2004) Inhibition and the right inferior frontal cortex. Trends Cogn Sci 8: 170-177. - PubMed
-
- Bolla KI, Ernst J, Mouratidis F, Funderbunk J, Matochik JA, Kurian V, Bragg J, Cadet JL, Kimes AS, London ED (2000) Reduced brain activation in chronic cocaine abusers during performance on the Stroop color-word interference task. Soc Neurosci Abstr 26: 482.12.
-
- Bolla KI, Ernst M, Mouratidis M, Matochik JA, Contoreggi C, Kurian V, Cadet JL, Kimes AS, Eldreth D, London ED (2001) Reduced cerebral blood flow in anterior cingulate cortex (ACC) during Stroop performance in chronic cocaine users. Hum Brain Mapp 13: 772.
-
- Bonson KR, Grant SJ, Contoreggi CS, Links JM, Metcalfe J, Weyl HL, Kurian V, Ernst M, London ED (2002) Neural systems and cue-induced cocaine craving. Neuropsychopharmacology 26: 376-386. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
