Interactions of postsynaptic density-95 and the NMDA receptor 2 subunit control calpain-mediated cleavage of the NMDA receptor
- PMID: 15590920
- PMCID: PMC6730266
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3722-04.2004
Interactions of postsynaptic density-95 and the NMDA receptor 2 subunit control calpain-mediated cleavage of the NMDA receptor
Abstract
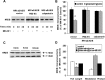
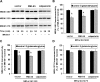
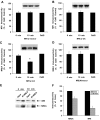
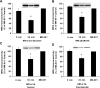
The calcium-dependent protease calpain cleaves the NMDA receptor 2 (NR2) subunit of the NMDA receptor both in vitro and in vivo and thus potentially modulates NMDA receptor function and turnover. We examined the ability of postsynaptic density-95 (PSD-95) protein to alter the calpain-mediated cleavage of NR2A and NR2B. Coexpression of PSD-95 with NMDA receptors in human embryonic kidney 293 cells blocked cleavage of NR2A and NR2B by NMDA receptor-activated calpain. NR2A cleavage by calpain occurred in the cell surface and intracellular fractions and required the presence of NR1 subunits. The blocking effect of PSD-95 did not result from decreased calpain activity, lowered intracellular calcium responses, or the blockade of internalization. Instead, this effect was eliminated by deletion of the C-terminal ESDV motif of NR2A or by overexpression of a palmitoylation-deficient PSD-95 mutant lacking the ability to cluster and to interact with NMDA receptors in situ, suggesting a role for association between the C terminus of NR2A and clustered PSD-95. Synapse-associated protein 102, a membrane-associated guanylate kinase interacting with NR2A but lacking palmitoylation motifs and the ability to cluster, did not protect NR2A from cleavage by calpain. Pharmacological inhibition of palmitoylation disrupted the interaction of PSD-95 with NMDA receptors in cortical neurons and allowed NR2A to be cleaved by calpain, whereas NR2A could not be cleaved in untreated neurons. These results indicate that PSD-95 clustering and direct association of NR2A and PSD-95 mediate the blocking effect of PSD-95 on calpain cleavage. PSD-95 could regulate the susceptibility of NMDA receptors to calpain-mediated cleavage during synaptic transmission and excitotoxicity.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Differential interaction of the tSXV motifs of the NR1 and NR2A NMDA receptor subunits with PSD-95 and SAP97.Eur J Neurosci. 1999 Jun;11(6):2031-43. doi: 10.1046/j.1460-9568.1999.00611.x. Eur J Neurosci. 1999. PMID: 10336672
-
Coexpression of postsynaptic density-95 protein with NMDA receptors results in enhanced receptor expression together with a decreased sensitivity to L-glutamate.J Neurochem. 2000 Dec;75(6):2501-10. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.2000.0752501.x. J Neurochem. 2000. PMID: 11080203
-
Excitotoxicity and focal cerebral ischemia induce truncation of the NR2A and NR2B subunits of the NMDA receptor and cleavage of the scaffolding protein PSD-95.Mol Psychiatry. 2008 Jan;13(1):99-114. doi: 10.1038/sj.mp.4002017. Epub 2007 May 8. Mol Psychiatry. 2008. PMID: 17486105
-
PSD-95: An Effective Target for Stroke Therapy Using Neuroprotective Peptides.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 22;22(22):12585. doi: 10.3390/ijms222212585. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34830481 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Calpain and the glutamatergic synapse.Front Biosci (Schol Ed). 2009 Jun 1;1(2):466-76. doi: 10.2741/s38. Front Biosci (Schol Ed). 2009. PMID: 19482714 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Soluble beta-amyloid1-40 induces NMDA-dependent degradation of postsynaptic density-95 at glutamatergic synapses.J Neurosci. 2005 Nov 30;25(48):11061-70. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3034-05.2005. J Neurosci. 2005. PMID: 16319306 Free PMC article.
-
Early disruption of the CREB pathway drives dendritic morphological alterations in FTD/ALS cortical neurons.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Dec 3;121(49):e2406998121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2406998121. Epub 2024 Nov 26. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 39589881 Free PMC article.
-
Selenoprotein K regulation of palmitoylation and calpain cleavage of ASAP2 is required for efficient FcγR-mediated phagocytosis.J Leukoc Biol. 2017 Feb;101(2):439-448. doi: 10.1189/jlb.2A0316-156RR. Epub 2016 Sep 6. J Leukoc Biol. 2017. PMID: 27601625 Free PMC article.
-
A novel protein complex in membrane rafts linking the NR2B glutamate receptor and autophagy is disrupted following traumatic brain injury.J Neurotrauma. 2009 May;26(5):703-20. doi: 10.1089/neu.2008.0783. J Neurotrauma. 2009. PMID: 19335206 Free PMC article.
-
Postsynaptic density-95 (PSD-95) and calcineurin control the sensitivity of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors to calpain cleavage in cortical neurons.Mol Pharmacol. 2008 Aug;74(2):360-70. doi: 10.1124/mol.108.046813. Epub 2008 Apr 29. Mol Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18445709 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anegawa NJ, Guttmann RP, Grant ER, Anand R, Lindstrom J, Lynch DR (2000) N-Methyl-d-aspartate receptor mediated toxicity in nonneuronal cell lines: characterization using fluorescent measures of cell viability and reactive oxygen species production. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 77: 163-175. - PubMed
-
- Bi R, Bi X, Baudry M (1998a) Phosphorylation regulates calpain-mediated truncation of glutamate ionotropic receptors. Brain Res 797: 154-158. - PubMed
-
- Bi X, Rong Y, Chen J, Dang S, Wang Z, Baudry M (1998b) Calpain-mediated regulation of NMDA receptor structure and function. Brain Res 790: 245-253. - PubMed
-
- Cho KO, Hunt CA, Kennedy MB (1992) The rat brain postsynaptic density fraction contains a homolog of the Drosophila discs-large tumor suppressor protein. Neuron 9: 929-942. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
