A "synaptoplasmic cistern" mediates rapid inhibition of cochlear hair cells
- PMID: 15590932
- PMCID: PMC6730265
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3674-04.2004
A "synaptoplasmic cistern" mediates rapid inhibition of cochlear hair cells
Abstract
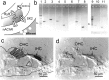
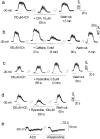
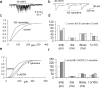
Cochlear hair cells are inhibited by cholinergic efferent neurons. The acetylcholine (ACh) receptor of the hair cell is a ligand-gated cation channel through which calcium enters to activate potassium channels and hyperpolarize the cell. It has been proposed that calcium-induced calcium release (CICR) from a near-membrane postsynaptic store supplements this process. Here, we demonstrate expression of type I ryanodine receptors in outer hair cells in the apical turn of the rat cochlea. Consistent with this finding, ryanodine and other store-active compounds alter the amplitude of transient currents produced by synaptic release of ACh, as well as the response of the hair cell to exogenous ACh. Like the sarcoplasmic reticulum of muscle, the "synaptoplasmic" cistern of the hair cell efficiently couples synaptic input to CICR.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Synaptic calcium regulation in hair cells of the chicken basilar papilla.J Neurosci. 2014 Dec 10;34(50):16688-97. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2615-14.2014. J Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25505321 Free PMC article.
-
BK channels mediate cholinergic inhibition of high frequency cochlear hair cells.PLoS One. 2010 Nov 4;5(11):e13836. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0013836. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 21079807 Free PMC article.
-
Onset of cholinergic efferent synaptic function in sensory hair cells of the rat cochlea.J Neurosci. 2011 Oct 19;31(42):15092-101. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2743-11.2011. J Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 22016543 Free PMC article.
-
A 'calcium capacitor' shapes cholinergic inhibition of cochlear hair cells.J Physiol. 2014 Aug 15;592(16):3393-401. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2013.267914. Epub 2014 Feb 24. J Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24566542 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulation of hair cell efferents.Hear Res. 2011 Sep;279(1-2):1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.heares.2010.12.018. Epub 2010 Dec 25. Hear Res. 2011. PMID: 21187136 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Efferent synaptic transmission at the vestibular type II hair cell synapse.J Neurophysiol. 2020 Aug 1;124(2):360-374. doi: 10.1152/jn.00143.2020. Epub 2020 Jul 1. J Neurophysiol. 2020. PMID: 32609559 Free PMC article.
-
Spatial patterns of noise-induced inner hair cell ribbon loss in the mouse mid-cochlea.iScience. 2024 Jan 8;27(2):108825. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.108825. eCollection 2024 Feb 16. iScience. 2024. PMID: 38313060 Free PMC article.
-
Calcium balance and mechanotransduction in rat cochlear hair cells.J Neurophysiol. 2010 Jul;104(1):18-34. doi: 10.1152/jn.00019.2010. Epub 2010 Apr 28. J Neurophysiol. 2010. PMID: 20427623 Free PMC article.
-
TRPC-like conductance mediates restoration of intracellular Ca2+ in cochlear outer hair cells in the guinea pig and rat.J Physiol. 2007 Feb 15;579(Pt 1):101-13. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2006.122929. Epub 2006 Dec 7. J Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17158171 Free PMC article.
-
Voltage-Gated Calcium Influx Modifies Cholinergic Inhibition of Inner Hair Cells in the Immature Rat Cochlea.J Neurosci. 2018 Jun 20;38(25):5677-5687. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0230-18.2018. Epub 2018 May 22. J Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29789373 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
