A role for MHC class I molecules in synaptic plasticity and regeneration of neurons after axotomy
- PMID: 15591351
- PMCID: PMC539738
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0408154101
A role for MHC class I molecules in synaptic plasticity and regeneration of neurons after axotomy
Abstract
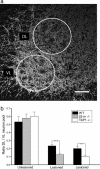
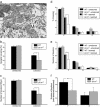
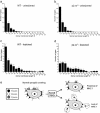
Recently, MHC class I molecules have been shown to be important for the retraction of synaptic connections that normally occurs during development [Huh, G.S., Boulanger, L. M., Du, H., Riquelme, P. A., Brotz, T. M. & Shatz, C. J. (2000) Science 290, 2155-2158]. In the adult CNS, a classical response of neurons to axon lesion is the detachment of synapses from the cell body and dendrites. We have investigated whether MHC I molecules are involved also in this type of synaptic detachment by studying the synaptic input to sciatic motoneurons at 1 week after peripheral nerve transection in beta2-microglobulin or transporter associated with antigen processing 1-null mutant mice, in which cell surface MHC I expression is impaired. Surprisingly, lesioned motoneurons in mutant mice showed more extensive synaptic detachments than those in wild-type animals. This surplus removal of synapses was entirely directed toward inhibitory synapses assembled in clusters. In parallel, a significantly smaller population of motoneurons reinnervated the distal stump of the transected sciatic nerve in mutants. MHC I molecules, which traditionally have been linked with immunological mechanisms, are thus crucial for a selective maintenance of synapses during the synaptic removal process in neurons after lesion, and the lack of MHC I expression may impede the ability of neurons to regenerate axons.
Figures

Comment in
-
Planting and pruning in the brain: MHC antigens involved in synaptic plasticity?Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Jan 4;102(1):3-4. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0408495101. Epub 2004 Dec 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 15623557 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Corriveau, R. A., Huh, G. S. & Shatz, C. J. (1998) Neuron 21 505-520. - PubMed
-
- Lindå, H., Hammarberg, H., Piehl, F., Khademi, M. & Olsson, T. (1999) J. Neuroimmunol. 101 76-86. - PubMed
-
- Blinzinger, K. & Kreutzberg, G. (1968) Z. Zellforsch. Mikrosk. Anat. 85 145-157. - PubMed
-
- Sumner, B. E. H. (1975) Exp. Neurol. 49 406-417. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

