Recombinant human interleukin 10 suppresses gliadin dependent T cell activation in ex vivo cultured coeliac intestinal mucosa
- PMID: 15591503
- PMCID: PMC1774366
- DOI: 10.1136/gut.2003.023150
Recombinant human interleukin 10 suppresses gliadin dependent T cell activation in ex vivo cultured coeliac intestinal mucosa
Abstract
Background: Enteropathy in coeliac disease (CD) is sustained by a gliadin specific Th1 response. Interleukin (IL)-10 can downregulate Th1 immune responses.
Aim: We investigated the ability of recombinant human (rh) IL-10 to suppress gliadin induced Th1 response.
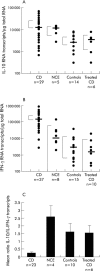
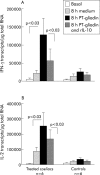
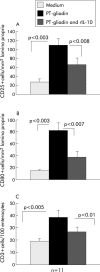
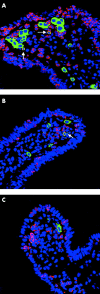
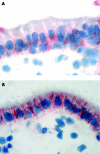
Patients and methods: IL-10 RNA transcripts were analysed by competitive reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction in duodenal biopsies from untreated and treated CD patients, non-coeliac enteropathies (NCE), and controls. CD biopsies were cultured with a peptic-tryptic digest of gliadin with or without rhIL-10. The proportion of CD80+ and CD25+ cells in the lamina propria, epithelial expression of Fas, intraepithelial infiltration of CD3+ cells, as well as cytokine synthesis (interferon gamma (IFN-gamma) and IL-2) were measured. Short term T cell lines (TCLs) obtained from treated CD biopsies cultured with gliadin with or without rhIL-10 were analysed by ELISPOT for gliadin specific production of IFN-gamma.
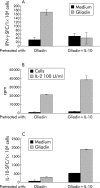
Results: In untreated CD and NCE, IL-10 RNA transcripts were significantly upregulated. In ex vivo organ cultures, rhIL-10 downregulated gliadin induced cytokine synthesis, inhibited intraepithelial migration of CD3+ cells, and reduced the proportion of lamina propria CD25+ and CD80+ cells whereas it did not interfere with epithelial Fas expression. In short term TCLs, rhIL-10 abrogated the IFN-gamma response to gliadin.
Conclusions: rhIL-10 suppresses gliadin specific T cell activation. It may interfere with the antigen presenting capacity of lamina propria mononuclear cells as it reduces the expression of CD80. Interestingly, rhIL-10 also induces a long term hyporesponsiveness of gliadin specific mucosal T cells. These results offer new perspectives for therapeutic strategies in coeliac patients based on immune modulation by IL-10.
Figures

References
-
- Schuppan D . Current concept of celiac disease pathogenesis. Gastroenterology 2000;119:234–42. - PubMed
-
- Nilsen EM, Frode LJ, Lundin KEA, et al. Gluten induces an intestinal cytokine response strongly dominated by interferon gamma in patients with celiac disease. Gastroenterology 1998;115:551–63. - PubMed
-
- Fiorentino DF, Zlotnik A, Vieira P, et al. IL-10 acts on the antigen-presenting cell to inhibit cytokine production by Th1 cells. J Immunol 1991;146:3444–51. - PubMed
-
- Fiorentino DF, Zlotnik A, Mosmann TR, et al. IL-10 inhibits cytokine production by activated macrophages. J Immunol 1991;147:3815–22. - PubMed
-
- de Waal Malefyt R , Haanen J, Spits H, et al. Interleukin 10 and viral IL-10 strongly reduce antigen-specific human T cell proliferation by diminishing the antigen-presenting capacity of monocytes via downregulation of class II major histocompatibility complex expression. J Exp Med 1991;174:915–24. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
