The product of the split ends gene is required for the maintenance of positional information during Drosophila development
- PMID: 15596016
- PMCID: PMC544560
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-213X-4-15
The product of the split ends gene is required for the maintenance of positional information during Drosophila development
Abstract
Background: The Drosophila split ends (spen) gene encodes a large nuclear protein containing three RNP-type RNA binding motifs, and a conserved transcriptional co-repressor-interacting domain at the C-terminus. Genetic analyses indicate that spen interacts with pathways that regulate the function of Hox proteins, the response to various signaling cascades and cell cycle control. Although spen mutants affect only a small subset of morphological structures in embryos, it has been difficult to find a common theme in spen mutant structural alterations, or in the interactions of spen with known signaling pathways.
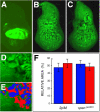
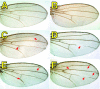
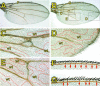
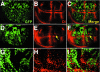
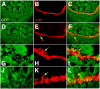
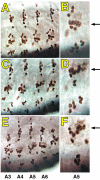
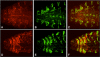
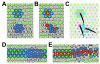
Results: By generating clones of spen mutant cells in wing imaginal discs, we show that spen function is required for the correct formation and positioning of veins and mechanosensory bristles both on the anterior wing margin and on the notum, and for the maintenance of planar polarity. Wing vein phenotypic alterations are enhanced by mutations in the crinkled (ck) gene, encoding a non-conventional myosin, and correlate with an abnormal spatial expression of Delta, an early marker of vein formation in third instar wing imaginal discs. Positioning defects were also evident in the organization of the embryonic peripheral nervous system, accompanied by abnormal E-Cadherin expression in the epidermis.
Conclusions: The data presented indicate that the role of spen is necessary to maintain the correct positioning of cells within a pre-specified domain throughout development. Its requirement for epithelial planar polarity, its interaction with ck, and the abnormal E-Cadherin expression associated with spen mutations suggest that spen exerts its function by interacting with basic cellular mechanisms required to maintain multicellular organization in metazoans. This role for spen may explain why mutations in this gene interact with the outcome of multiple signaling pathways.
Figures



Similar articles
-
spen encodes an RNP motif protein that interacts with Hox pathways to repress the development of head-like sclerites in the Drosophila trunk.Development. 1999 Dec;126(23):5373-85. doi: 10.1242/dev.126.23.5373. Development. 1999. PMID: 10556062
-
jing is required for wing development and to establish the proximo-distal axis of the leg in Drosophila melanogaster.Genetics. 2006 May;173(1):255-66. doi: 10.1534/genetics.106.056341. Epub 2006 Mar 1. Genetics. 2006. PMID: 16510782 Free PMC article.
-
The Ecdysone and Notch Pathways Synergistically Regulate Cut at the Dorsal-Ventral Boundary in Drosophila Wing Discs.J Genet Genomics. 2016 Apr 20;43(4):179-86. doi: 10.1016/j.jgg.2016.03.002. Epub 2016 Mar 17. J Genet Genomics. 2016. PMID: 27117286 Free PMC article.
-
Pattern formation in the Drosophila wing: The development of the veins.Bioessays. 2003 May;25(5):443-51. doi: 10.1002/bies.10258. Bioessays. 2003. PMID: 12717815 Review.
-
Forces shaping the Drosophila wing.Mech Dev. 2017 Apr;144(Pt A):23-32. doi: 10.1016/j.mod.2016.10.003. Epub 2016 Oct 23. Mech Dev. 2017. PMID: 27784612 Review.
Cited by
-
Chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan Windpipe modulates Hedgehog signaling in Drosophila.Mol Biol Cell. 2020 Apr 1;31(8):813-824. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E19-06-0327. Epub 2020 Feb 12. Mol Biol Cell. 2020. PMID: 32049582 Free PMC article.
-
Split ends antagonizes the Notch and potentiates the EGFR signaling pathways during Drosophila eye development.Mech Dev. 2007 Sep-Oct;124(9-10):792-806. doi: 10.1016/j.mod.2007.05.002. Epub 2007 May 21. Mech Dev. 2007. PMID: 17588724 Free PMC article.
-
The Spen homolog Msx2-interacting nuclear target protein interacts with the E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme UbcH8.Mol Cell Biochem. 2006 Aug;288(1-2):151-7. doi: 10.1007/s11010-006-9131-9. Epub 2006 Apr 1. Mol Cell Biochem. 2006. PMID: 16583136
-
SPOC domain proteins in health and disease.Genes Dev. 2023 Mar 1;37(5-6):140-170. doi: 10.1101/gad.350314.122. Epub 2023 Mar 16. Genes Dev. 2023. PMID: 36927757 Free PMC article. Review.
-
spenito is required for sex determination in Drosophila melanogaster.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Sep 15;112(37):11606-11. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1515891112. Epub 2015 Aug 31. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 26324914 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gellon G, Harding KW, McGinnis N, Martin M, McGinnis W. A genetic screen for modifiers of Deformed homeotic function identifies novel genes required for head development. Development. 1997;124:3321–3331. - PubMed
-
- Wiellette EL, Harding KW, Mace KA, Ronshaugen MR, Wang FY, McGinnis W. spen encodes an RNP motif protein that interacts with Hox pathways to repress the development of head-like sclerites in the Drosophila trunk. Development. 1999;126:5373–5385. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

