Implication of proprotein convertases in the processing and spread of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus
- PMID: 15596135
- PMCID: PMC7092861
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.11.063
Implication of proprotein convertases in the processing and spread of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus
Abstract
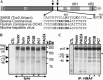
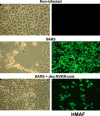
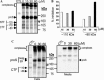
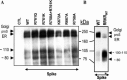
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV) is the etiological agent of SARS. Analysis of SARS-CoV spike glycoprotein (S) using recombinant plasmid and virus infections demonstrated that the S-precursor (proS) exists as a approximately 190 kDa endoplasmic reticulum form and a approximately 210 kDa Golgi-modified form. ProS is subsequently processed into two C-terminal proteins of approximately 110 and approximately 80 kDa. The membrane-bound proprotein convertases (PCs) furin, PC7 or PC5B enhanced the production of the approximately 80 kDa protein. In agreement, proS processing, cytopathic effects, and viral titers were enhanced in recombinant Vero E6 cells overexpressing furin, PC7 or PC5B. The convertase inhibitor dec-RVKR-cmk significantly reduced proS cleavage and viral titers of SARS-CoV infected cells. In addition, inhibition of processing by dec-RVKR-cmk completely abrogated the virus-induced cellular cytopathicity. A fluorogenically quenched synthetic peptide encompassing Arg(761) of the spike glycoprotein was efficiently cleaved by furin and the cleavage was inhibited by EDTA and dec-RVKR-cmk. Taken together, our data indicate that furin or PC-mediated processing plays a critical role in SARS-CoV spread and cytopathicity, and inhibitors of the PCs represent potential therapeutic anti-SARS-CoV agents.
Figures

References
-
- Ksiazek T.G., Erdman D., Goldsmith C.S., Zaki S.R., Peret T., Emery S., Tong S., Urbani C., Comer J.A., Lim W., Rollin P.E, Dowell S.F., Ling A.E., Humphrey C.D., Shieh W.J., Guarner J., Paddock C.D., Rota P., Fields B., DeRisi J., Yang J.Y., Cox N., Hughes J.M., LeDuc J.W., Bellini W.J., Anderson L.J. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003;348:1953–1966. - PubMed
-
- Marra M.A., Jones S.J., Astell C.R., Holt R.A., Brooks-Wilson A., Butterfield Y.S., Khattra J., Asano J.K., Barber S.A., Chan S.Y., Cloutier A., Coughlin S.M., Freeman D., Girn N., Griffith O.L., Leach S.R., Mayo M., McDonald H., Montgomery S.B., Pandoh P.K., Petrescu A.S., Robertson A.G., Schein J.E., Siddiqui A., Smailus D.E., Stott J.M., Yang G.S., Plummer F., Andonov A., Artsob H., Bastien N., Bernard K., Booth T.F., Bowness D., Czub M., Drebot M., Fernando L., Flick R., Garbutt M., Gray M., Grolla A., Jones S., Feldmann H., Meyers A., Kabani A., Li Y., Normand S., Stroher U., Tipples G.A., Tyler S., Vogrig R., Ward D., Watson B., Brunham R.C., Krajden M., Petric M., Skowronski D.M., Upton C., Roper R.L. Science. 2003;300:1399–1404. - PubMed
-
- Rota P.A., Oberste M.S., Monroe S.S., Nix W.A., Campagnoli R., Icenogle J.P., Penaranda S., Bankamp B., Maher K., Chen M.H., Tong S., Tamin A., Lowe L., Frace M., DeRisi J.L., Chen Q., Wang D., Erdman D.D., Peret T.C., Burns C., Ksiazek T.G., Rollin P.E., Sanchez A., Liffick S., Holloway B., Limor J., McCaustland K., Olsen-Rasmussen M., Fouchier R., Gunther S., Osterhaus A.D., Drosten C., Pallansch M.A., Anderson L.J., Bellini W.J. Science. 2003;300:1394–1399. - PubMed
-
- Ng M.L., Tan S.H., See E.E., Ooi E.E., Ling A.E. J. Gen. Virol. 2003;84:3291–3303. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

