Effects of insulin and transgenic overexpression of UDP-glucose pyrophosphorylase on UDP-glucose and glycogen accumulation in skeletal muscle fibers
- PMID: 15596435
- PMCID: PMC1482786
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M413614200
Effects of insulin and transgenic overexpression of UDP-glucose pyrophosphorylase on UDP-glucose and glycogen accumulation in skeletal muscle fibers
Abstract
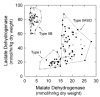
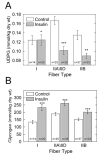
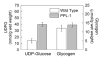
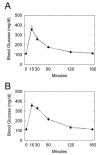
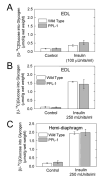
UDP-glucose (UDP-Glc) and glycogen levels in skeletal muscle fibers of defined fiber type were measured using microanalytical methods. Infusing rats with insulin increased glycogen in both Type I and Type II fibers. Insulin was without effect on UDP-Glc in Type I fibers but decreased UDP-Glc by 35-40% in Type IIA/D and Type IIB fibers. The reduction in UDP-Glc suggested that UDP-Glc pyrophosphorylase (PPL) activity might limit glycogen synthesis in response to insulin. To explore this possibility, we generated mice overexpressing a UDP-Glc PPL transgene in skeletal muscle. The transgene increased both UDP-Glc PPL activity and levels of UDP-Glc in skeletal muscles by approximately 3-fold. However, overexpression of UDP-Glc PPL was without effect on either the levels of skeletal muscle glycogen or glucose tolerance in vivo. The transgene was also without effect on either control or insulin-stimulated rates of (14)C-glucose incorporation into glycogen in muscles incubated in vitro. The results indicate that UDP-Glc PPL activity is not limiting for glycogen synthesis.
Figures
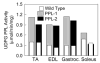

Similar articles
-
Control of glycogen synthesis is shared between glucose transport and glycogen synthase in skeletal muscle fibers.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2000 Feb;278(2):E234-43. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.2000.278.2.E234. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2000. PMID: 10662707
-
A point mutation in the UDP-glucose pyrophosphorylase gene results in decreases of UDP-glucose and inactivation of glycogen synthase.Biochem J. 2003 Mar 15;370(Pt 3):995-1001. doi: 10.1042/BJ20021320. Biochem J. 2003. PMID: 12460121 Free PMC article.
-
UDP-glucose pyrophosphorylase influences polysaccharide synthesis, cell wall components, and hyphal branching in Ganoderma lucidum via regulation of the balance between glucose-1-phosphate and UDP-glucose.Fungal Genet Biol. 2015 Sep;82:251-63. doi: 10.1016/j.fgb.2015.07.012. Epub 2015 Jul 31. Fungal Genet Biol. 2015. PMID: 26235043
-
Exploring the active site in UDP-glucose pyrophosphorylase by affinity labelling and site-directed mutagenesis.Biotechnol Appl Biochem. 1993 Oct;18(2):209-16. Biotechnol Appl Biochem. 1993. PMID: 8251118 Review.
-
Regulation of muscle glycogen synthase phosphorylation and kinetic properties by insulin, exercise, adrenaline and role in insulin resistance.Arch Physiol Biochem. 2009 Feb;115(1):13-21. doi: 10.1080/13813450902778171. Arch Physiol Biochem. 2009. PMID: 19267278 Review.
Cited by
-
RNA sequencing for global gene expression associated with muscle growth in a single male modern broiler line compared to a foundational Barred Plymouth Rock chicken line.BMC Genomics. 2017 Jan 13;18(1):82. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-3471-y. BMC Genomics. 2017. PMID: 28086790 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of acute exercise on glycogen synthase in muscle from obese and diabetic subjects.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2012 Jul 1;303(1):E82-9. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00658.2011. Epub 2012 Apr 17. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2012. PMID: 22510711 Free PMC article.
-
Gain of function AMP-activated protein kinase γ3 mutation (AMPKγ3R200Q) in pig muscle increases glycogen storage regardless of AMPK activation.Physiol Rep. 2016 Jun;4(11):e12802. doi: 10.14814/phy2.12802. Physiol Rep. 2016. PMID: 27302990 Free PMC article.
-
Two Homologous Enzymes of the GalU Family in Rhodococcus opacus 1CP-RoGalU1 and RoGalU2.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Nov 19;20(22):5809. doi: 10.3390/ijms20225809. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31752319 Free PMC article.
-
A century of exercise physiology: key concepts in regulation of glycogen metabolism in skeletal muscle.Eur J Appl Physiol. 2022 Aug;122(8):1751-1772. doi: 10.1007/s00421-022-04935-1. Epub 2022 Mar 30. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35355125 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

