Mechanisms and control of rapid genomic changes in flax
- PMID: 15596467
- PMCID: PMC4246718
- DOI: 10.1093/aob/mci013
Mechanisms and control of rapid genomic changes in flax
Abstract
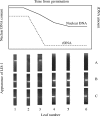
Background and aims: The nuclear DNA of certain varieties of flax (Linum usitatissimum) can vary within a single generation when the plants are grown under specific environmental conditions. This review details the genomic variations that have been identified and associated with this environmental response.
Conclusions: The variation occurs across the whole spectrum of sequence repetition and has been shown to occur in the highly repeated, middle repetitive and low copy number sequences. Although the variation has been shown to be spread throughout the genome it does not occur at random, as similar molecular events have been shown to occur repeatedly. The changes in two labile regions in the nucleus, the ribosomal RNA genes and a site-specific insertion event, have been shown to occur within the period of vegetative growth and over a relatively short period of that growth. The gradual change in total nuclear DNA that has been described would then need to have arisen through an accumulation of changes occurring over the whole, or most of the, period of growth prior to flowering. The polymorphisms that result from these rapidly occurring genomic events have also been observed in many other flax and linseed varieties as well as in the wild progenitors of flax.
Figures
Similar articles
-
RAPD polymorphisms detected among the flax genotrophs.Plant Mol Biol. 1999 Dec;41(6):795-800. doi: 10.1023/a:1006385606163. Plant Mol Biol. 1999. PMID: 10737144
-
A site-specific insertion sequence in flax genotrophs induced by environment.New Phytol. 2005 Jul;167(1):171-80. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2005.01398.x. New Phytol. 2005. PMID: 15948840
-
Genetic characterization of a core collection of flax (Linum usitatissimum L.) suitable for association mapping studies and evidence of divergent selection between fiber and linseed types.BMC Plant Biol. 2013 May 6;13:78. doi: 10.1186/1471-2229-13-78. BMC Plant Biol. 2013. PMID: 23647851 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide identification of ATP binding cassette (ABC) transporter and heavy metal associated (HMA) gene families in flax (Linum usitatissimum L.).BMC Genomics. 2020 Oct 19;21(1):722. doi: 10.1186/s12864-020-07121-9. BMC Genomics. 2020. PMID: 33076828 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Advances to Combat Different Biotic and Abiotic Stresses in Linseed (Linum usitatissimum L.): A Comprehensive Review.Genes (Basel). 2023 Jul 17;14(7):1461. doi: 10.3390/genes14071461. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37510365 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Drought-induced site-specific DNA methylation and its association with drought tolerance in rice (Oryza sativa L.).J Exp Bot. 2011 Mar;62(6):1951-60. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erq391. Epub 2010 Dec 30. J Exp Bot. 2011. PMID: 21193578 Free PMC article.
-
Ribosomal DNA deletions modulate genome-wide gene expression: "rDNA-sensitive" genes and natural variation.PLoS Genet. 2011 Apr;7(4):e1001376. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1001376. Epub 2011 Apr 21. PLoS Genet. 2011. PMID: 21533076 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide negative feedback drives transgenerational DNA methylation dynamics in Arabidopsis.PLoS Genet. 2015 Apr 22;11(4):e1005154. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005154. eCollection 2015 Apr. PLoS Genet. 2015. PMID: 25902052 Free PMC article.
-
Phylogenomic analysis of UDP glycosyltransferase 1 multigene family in Linum usitatissimum identified genes with varied expression patterns.BMC Genomics. 2012 May 8;13:175. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-13-175. BMC Genomics. 2012. PMID: 22568875 Free PMC article.
-
Like father like son. A fresh review of the inheritance of acquired characteristics.EMBO Rep. 2007 Sep;8(9):798-803. doi: 10.1038/sj.embor.7401060. EMBO Rep. 2007. PMID: 17767188 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Bassi P. 1990. Quantitative variation of nuclear DNA during plant development: A critical analysis. Biological Reviews 65: 185–225.
-
- Bassi P. 1991. Repetitive non-coding DNA: A possible link between environment and gene expression in plants? Biologisches Zentralblatt 110: 1–13.
-
- Chen Y. 1999.An insertion sequence in flax induced by the environment. PhD Thesis, Case Western Reserve University, USA.
-
- Cullis CA. 1973. DNA differences between flax genotypes. Nature 243: 515–516. - PubMed
-
- Cullis CA. 1976. Environmentally induced changes in ribosomal RNA cistron number in flax. Heredity 36: 73–79. - PubMed

