Desmosterol may replace cholesterol in lipid membranes
- PMID: 15596512
- PMCID: PMC1305238
- DOI: 10.1529/biophysj.104.048926
Desmosterol may replace cholesterol in lipid membranes
Abstract
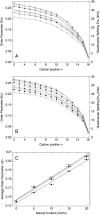
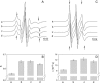
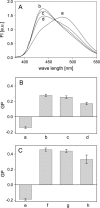
Recently, knockout mice entirely lacking cholesterol have been described as showing only a mild phenotype. For these animals, synthesis of cholesterol was interrupted at the level of its immediate precursor, desmosterol. Since cholesterol is a major and essential constituent of mammalian cellular membranes, we asked whether cholesterol with its specific impact on membrane properties might be replaced by desmosterol. By employing various approaches of NMR, fluorescence, and EPR spectroscopy, we found that the properties of phospholipid membranes like lipid packing in the presence of cholesterol or desmosterol are very similar. However, for lanosterol, a more distant precursor of cholesterol synthesis, we found significant differences in comparison with cholesterol and desmosterol. Our results show that, from the point of view of membrane biophysics, cholesterol and desmosterol behave identically and, therefore, replacement of cholesterol by desmosterol may not impact organism homeostasis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Diffusion of cholesterol and its precursors in lipid membranes studied by 1H pulsed field gradient magic angle spinning NMR.Biophys J. 2005 Oct;89(4):2504-12. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.105.062018. Epub 2005 Aug 5. Biophys J. 2005. PMID: 16085761 Free PMC article.
-
The influence of cholesterol precursor--desmosterol--on artificial lipid membranes.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 Aug;1848(8):1639-45. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2015.04.017. Epub 2015 May 7. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 25960185
-
Comparison of cholesterol and its direct precursors along the biosynthetic pathway: effects of cholesterol, desmosterol and 7-dehydrocholesterol on saturated and unsaturated lipid bilayers.J Chem Phys. 2008 Oct 21;129(15):154508. doi: 10.1063/1.2996296. J Chem Phys. 2008. PMID: 19045210
-
Liquid-liquid immiscibility in membranes.Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 2003;32:469-92. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biophys.32.110601.141704. Epub 2003 Jan 31. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 2003. PMID: 12574063 Review.
-
The state of lipid rafts: from model membranes to cells.Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 2003;32:257-83. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biophys.32.110601.142439. Epub 2003 Jan 16. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 2003. PMID: 12543707 Review.
Cited by
-
Holmium Complex with Phospholipids as 1H NMR Relaxational Sensor of Temperature and Viscosity.Molecules. 2022 Oct 8;27(19):6691. doi: 10.3390/molecules27196691. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36235229 Free PMC article.
-
From cholesterogenesis to steroidogenesis: role of riboflavin and flavoenzymes in the biosynthesis of vitamin D.Adv Nutr. 2014 Mar 1;5(2):144-63. doi: 10.3945/an.113.005181. Adv Nutr. 2014. PMID: 24618756 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DHCR24 inhibitor SH42 increases desmosterol without preventing atherosclerosis development in mice.iScience. 2024 Apr 26;27(6):109830. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.109830. eCollection 2024 Jun 21. iScience. 2024. PMID: 38770137 Free PMC article.
-
Cholesterol mediated ferroptosis suppression reveals essential roles of Coenzyme Q and squalene.Commun Biol. 2023 Nov 1;6(1):1108. doi: 10.1038/s42003-023-05477-8. Commun Biol. 2023. PMID: 37914914 Free PMC article.
-
Cholesterol's aliphatic side chain modulates membrane properties.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2013 Dec 2;52(49):12848-51. doi: 10.1002/anie.201306753. Epub 2013 Nov 25. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2013. PMID: 24382636 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Albert, A. D., J. E. Young, and P. L. Yeagle. 1996. Rhodopsin-cholesterol interactions in bovine rod outer segment disk membranes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1285:47–55. - PubMed
-
- Anderson, R. G. W., and K. Jacobson. 2002. A role for lipid shells in targeting proteins to caveolae, rafts, and other lipid domains. Science. 296:1821–1825. - PubMed
-
- Ayala-Sanmartin, J. 2001. Cholesterol enhances phospholipid binding and aggregation of annexins by their core domain. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 283:72–79. - PubMed
-
- Bloch, K. 1983. Sterol structure and membrane function. CRC Crit. Rev. Biochem. 14:47–92. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

