Muscle ring finger protein-1 inhibits PKC{epsilon} activation and prevents cardiomyocyte hypertrophy
- PMID: 15596539
- PMCID: PMC2172633
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.200402033
Muscle ring finger protein-1 inhibits PKC{epsilon} activation and prevents cardiomyocyte hypertrophy
Abstract
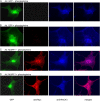
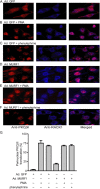
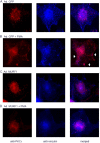
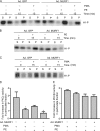
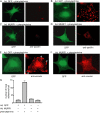
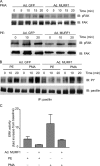
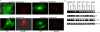
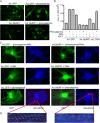
Much effort has focused on characterizing the signal transduction cascades that are associated with cardiac hypertrophy. In spite of this, we still know little about the mechanisms that inhibit hypertrophic growth. We define a novel anti-hypertrophic signaling pathway regulated by muscle ring finger protein-1 (MURF1) that inhibits the agonist-stimulated PKC-mediated signaling response in neonatal rat ventricular myocytes. MURF1 interacts with receptor for activated protein kinase C (RACK1) and colocalizes with RACK1 after activation with phenylephrine or PMA. Coincident with this agonist-stimulated interaction, MURF1 blocks PKCepsilon translocation to focal adhesions, which is a critical event in the hypertrophic signaling cascade. MURF1 inhibits focal adhesion formation, and the activity of downstream effector ERK1/2 is also inhibited in the presence of MURF1. MURF1 inhibits phenylephrine-induced (but not IGF-1-induced) increases in cell size. These findings establish that MURF1 is a key regulator of the PKC-dependent hypertrophic response and can blunt cardiomyocyte hypertrophy, which may have important implications in the pathophysiology of clinical cardiac hypertrophy.
Figures

References
-
- Allo, S.N., L.L. Carl, and H.E. Morgan. 1992. Acceleration of growth of cultured cardiomyocytes and translocation of protein kinase C. Am. J. Physiol. 263:C319–C325. - PubMed
-
- Besson, A., T.L. Wilson, and V.W. Yong. 2002. The anchoring protein RACK1 links protein kinase Cε to integrin β chains. Requirement for adhesion and motility. J. Biol. Chem. 277:22073–22084. - PubMed
-
- Bodine, S.C., E. Latres, S. Baumhueter, V.K. Lai, L. Nunez, B.A. Clarke, W.T. Poueymirou, F.J. Panaro, E. Na, K. Dharmarajan, et al. 2001. a. Identification of ubiquitin ligases required for skeletal muscle atrophy. Science. 294:1704–1708. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

