Major reduction of atherosclerosis in fractalkine (CX3CL1)-deficient mice is at the brachiocephalic artery, not the aortic root
- PMID: 15596719
- PMCID: PMC539720
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0408096101
Major reduction of atherosclerosis in fractalkine (CX3CL1)-deficient mice is at the brachiocephalic artery, not the aortic root
Abstract
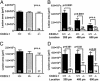
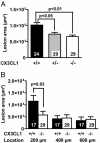
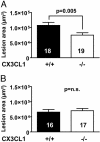
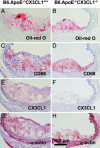
Fractalkine (CX3CL1) is of particular interest in atherogenesis because it can serve as an adhesion molecule and a chemokine. Fractalkine and its receptor CX3CR1 are expressed in atherosclerotic lesions of humans and mice. However, the effect of fractalkine deficiency on atherosclerosis susceptibility is unknown. Fractalkine-deficient mice on the C57BL/6 (B6) background were bred to the atherosclerosis-sensitizing B6.ApoE(-/-) and B6.LDLR(-/-) backgrounds. Compared with controls, aortic-root lesion area was unchanged in fractalkine-deficient male and female B6.ApoE(-/-) mice at 16 weeks of age and males at 12 weeks of age, but it was mildly reduced (30%, P = 0.005) in females at 12 weeks of age. In contrast, lesion area at the brachiocephalic artery (BCA) was reduced dramatically by approximately 85% in fractalkine-deficient females [42,251 +/- 26,136 microm(2) (n = 15) vs. 6,538 +/- 11,320 microm(2);(n = 24), P < 0.0001] and males [36,911 +/- 32,504 microm(2) (n = 24) vs. 6,768 +/- 8,595 microm(2) (n = 14); P = 0.001] at 16 weeks of age. Fractalkine-deficient B6.ApoE(-/-) mice were comparable with controls in body weight, plasma cholesterol, plasma high-density lipoprotein cholesterol and white blood cell counts. On the B6.LDLR(-/-) background, lesion areas were reduced by 35% at the aortic root (P < 0.01) and by 50% at the BCA (P < 0.05) in fractalkine-deficient females at 16 weeks of age. Lesions in fractalkine-deficient mice on the B6.ApoE(-/-) and B6.LDLR(-/-) backgrounds were less complex and contained significantly fewer macrophages than controls. In conclusion, the major reduction of atherosclerosis in fractalkine-deficient mice appears to be at the BCA rather than the aortic root.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

