Analysis of wild-type and mutant SL3-3 murine leukemia virus insertions in the c-myc promoter during lymphomagenesis reveals target site hot spots, virus-dependent patterns, and frequent error-prone gap repair
- PMID: 15596802
- PMCID: PMC538719
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.79.1.67-78.2005
Analysis of wild-type and mutant SL3-3 murine leukemia virus insertions in the c-myc promoter during lymphomagenesis reveals target site hot spots, virus-dependent patterns, and frequent error-prone gap repair
Abstract
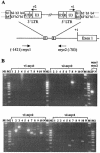
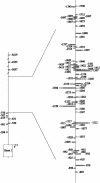
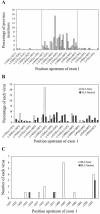
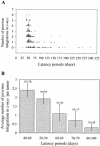
The murine leukemia retrovirus SL3-3 induces lymphomas in the T-cell compartment of the hematopoetic system when it is injected into newborn mice of susceptible strains. Previously, our laboratory reported on a deletion mutant of SL3-3 that induces T-cell tumors faster than the wild-type virus (S. Ethelberg, A. B. Sorensen, J. Schmidt, A. Luz, and F. S. Pedersen, J. Virol. 71:9796-9799, 1997). PCR analyses of proviral integrations in the promoter region of the c-myc proto-oncogene in lymphomas induced by wild-type SL3-3 [SL3-3(wt)] and the enhancer deletion mutant displayed a difference in targeting frequency into this locus. We here report on patterns of proviral insertions into the c-myc promoter region from SL3-3(wt), the faster variant, as well as other enhancer variants from a total of approximately 250 tumors. The analysis reveals (i) several integration site hot spots in the c-myc promoter region, (ii) differences in integration patterns between SL3-3(wt) and enhancer deletion mutant viruses, (iii) a correlation between tumor latency and the number of proviral insertions into the c-myc promoter, and (iv) a [5'-(A/C/G)TA(C/G/T)-3'] integration site consensus sequence. Unexpectedly, about 12% of the sequenced insertions were associated with point mutations in the direct repeat flanking the provirus. Based on these results, we propose a model for error-prone gap repair of host-provirus junctions.
Figures

References
-
- Agresti, A. 1990. Categorical data analysis. Wiley, New York, N.Y.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

