Macrophages kill human papillomavirus type 16 E6-expressing tumor cells by tumor necrosis factor alpha- and nitric oxide-dependent mechanisms
- PMID: 15596807
- PMCID: PMC538740
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.79.1.116-123.2005
Macrophages kill human papillomavirus type 16 E6-expressing tumor cells by tumor necrosis factor alpha- and nitric oxide-dependent mechanisms
Abstract
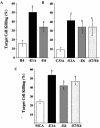
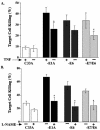
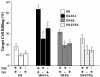
The expression of adenovirus serotype 2 or 5 (Ad2/5) E1A sensitizes cells to killing by NK cells and activated macrophages, a property that correlates with the ability of E1A to bind the transcriptional coadaptor proteins p300-CBP. The E6 oncoproteins derived from the high-risk human papillomaviruses (HPV) interact with p300 and can complement mutant forms of E1A that cannot interact with p300 to induce cellular immortalization. Therefore, we determined if HPV type 16 (HPV16) E6 could sensitize cells to killing by macrophages and NK cells. HPV16 E6 expression sensitized human (H4 and C33A) and murine (MCA-102) cell lines to lysis by macrophages but not by NK cells. The lysis of cells that expressed E6 by macrophages was p53 independent but dependent on the production of tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) or nitric oxide (NO) by macrophages. Unlike cytolysis assays with macrophages, E6 expression did not significantly sensitize cells to lysis by the direct addition of NO or TNF-alpha. Like E1A, E6 has been reported to sensitize cells to lysis by TNF-alpha by inhibiting the TNF-alpha-induced activation of NF-kappaB. We found that E1A, but not E6, blocked the TNF-alpha-induced activation of NF-kappaB, an activity that correlated with E1A-p300 binding. In summary, Ad5 E1A and HPV16 E6 sensitized cells to lysis by macrophages. Unlike E1A, E6 did not block the ability of TNF-alpha to activate NF-kappaB or sensitize cells to lysis by NK cells, TNF-alpha, or NO. Thus, there appears to be a spectrum of common and unique biological activities that result as a consequence of the interaction of E6 or E1A with p300-CBP.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Adenovirus E1A, not human papillomavirus E7, sensitizes tumor cells to lysis by macrophages through nitric oxide- and TNF-alpha-dependent mechanisms despite up-regulation of 70-kDa heat shock protein.J Immunol. 2003 Apr 15;170(8):4119-26. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.170.8.4119. J Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12682242
-
Expression of an E1A/E7 chimeric protein sensitizes tumor cells to killing by activated macrophages but not NK cells.J Virol. 2004 May;78(9):4646-54. doi: 10.1128/jvi.78.9.4646-4654.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 15078947 Free PMC article.
-
Complementation of a p300/CBP defective-binding mutant of adenovirus E1a by human papillomavirus E6 proteins.J Gen Virol. 2002 Apr;83(Pt 4):829-833. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-83-4-829. J Gen Virol. 2002. PMID: 11907332
-
Adenovirus serotype 5 E1A sensitizes tumor cells to NKG2D-dependent NK cell lysis and tumor rejection.J Exp Med. 2005 Dec 5;202(11):1477-82. doi: 10.1084/jem.20050240. Epub 2005 Nov 28. J Exp Med. 2005. PMID: 16314433 Free PMC article.
-
Oncogenicity of human papillomavirus- or adenovirus-transformed cells correlates with resistance to lysis by natural killer cells.J Virol. 1995 Dec;69(12):7639-47. doi: 10.1128/JVI.69.12.7639-7647.1995. J Virol. 1995. PMID: 7494272 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Profiling of miRNAs in Mouse Peritoneal Macrophages Responding to Echinococcus multilocularis Infection.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020 Apr 3;10:132. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.00132. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32309217 Free PMC article.
-
The Host-Microbe Interplay in Human Papillomavirus-Induced Carcinogenesis.Microorganisms. 2019 Jul 13;7(7):199. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms7070199. Microorganisms. 2019. PMID: 31337018 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of IL-10 and TGF-β1 in local immunosuppression in HPV-associated cervical neoplasia.World J Clin Oncol. 2014 Oct 10;5(4):753-63. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v5.i4.753. World J Clin Oncol. 2014. PMID: 25302175 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oral Papillomatosis: Its Relation with Human Papilloma Virus Infection and Local Immunity-An Update.Medicina (Kaunas). 2022 Aug 15;58(8):1103. doi: 10.3390/medicina58081103. Medicina (Kaunas). 2022. PMID: 36013570 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunopotentiator Aikejia improves the therapeutic efficacy of PD-1/PD-L1 immunosuppressive pathway in CT26.WT cancer cell.J Cancer. 2019 Jun 9;10(15):3472-3480. doi: 10.7150/jca.29672. eCollection 2019. J Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31293651 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arany, Z., W. R. Sellers, D. M. Livingston, and R. Eckner. 1994. E1A-associated p300 and CREB-associated CBP belong to a conserved family of coactivators. Cell 77:799-800. - PubMed
-
- Bernat, A., N. Avvakumov, J. S. Mymryk, and L. Banks. 2003. Interaction between the HPV E7 oncoprotein and the transcriptional coactivator p300. Oncogene 22:5927-5937. - PubMed
-
- Bernat, A., P. Massimi, and L. Banks. 2002. Complementation of a p300/CBP defective-binding mutant of adenovirus E1a by human papillomavirus E6 proteins. J. Gen. Virol. 83:829-833. - PubMed
-
- Bosch, F. X., M. M. Manos, N. Muñoz, M. Sherman, A. M. Jansen, J. Peto, M. H. Schiffman, V. Moreno, R. Kurman, and K. V. Shah. 1995. Prevalence of human papillomavirus in cervical cancer: a worldwide perspective. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 87:796-802. - PubMed
-
- Brokaw, J. L., C. L. Yee, and K. Münger. 1994. A mutational analysis of the amino terminal domain of the human papillomavirus type 16 E7 oncoprotein. Virology 205:603-607. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

