Defective interfering RNA hinders the activity of a tombusvirus-encoded posttranscriptional gene silencing suppressor
- PMID: 15596838
- PMCID: PMC538711
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.79.1.450-457.2005
Defective interfering RNA hinders the activity of a tombusvirus-encoded posttranscriptional gene silencing suppressor
Abstract
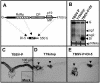
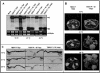
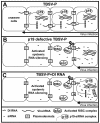
Defective interfering (DI) RNAs are subviral replicons originating from the viral genome and are associated with many plant RNA viruses and nearly all animal RNA viruses. The presence of DI RNAs in tombusvirus-infected plants reduces the accumulation of helper virus RNA and results in the development of attenuated symptoms similar to those caused by tombusviruses defective in p19, the posttranscriptional gene silencing (PTGS) suppressor. In situ analysis of infected plants containing DI RNAs revealed that the extent of virus infection was spatially restricted as was found for p19-defective tombusvirus. Previously, p19 was shown to suppress PTGS by sequestering the small interfering RNAs (siRNAs), which act as the specificity determinant for PTGS. Our results demonstrate that DI RNAs dramatically elevate the level of virus-specific siRNAs in viral infections, resulting in the saturation of p19 and the accumulation of unbound siRNAs. Moreover, we showed that, at low temperature, where PTGS is inhibited, DI RNAs are not able to efficiently interfere with virus accumulation and protect the plants. These data show that the activation of PTGS plays a pivotal role in DI RNA-mediated interference. Our data also support a role for 21-nucleotide siRNAs in PTGS signaling.
Figures


Similar articles
-
In situ characterization of Cymbidium Ringspot Tombusvirus infection-induced posttranscriptional gene silencing in Nicotiana benthamiana.J Virol. 2003 May;77(10):6082-6. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.10.6082-6086.2003. J Virol. 2003. PMID: 12719602 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of sequence elements of tombusvirus-associated defective interfering RNAs required for symptom modulation.Arch Virol. 2006 Mar;151(3):625-33. doi: 10.1007/s00705-005-0651-5. Epub 2005 Nov 17. Arch Virol. 2006. PMID: 16328149
-
Tombusvirus P19-mediated suppression of virus-induced gene silencing is controlled by genetic and dosage features that influence pathogenicity.Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2002 Mar;15(3):269-80. doi: 10.1094/MPMI.2002.15.3.269. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2002. PMID: 11952130
-
Effects and side-effects of viral RNA silencing suppressors on short RNAs.Trends Plant Sci. 2004 Feb;9(2):76-83. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2003.12.010. Trends Plant Sci. 2004. PMID: 15102373 Review.
-
Studying the RNA silencing pathway with the p19 protein.FEBS Lett. 2013 Apr 17;587(8):1198-205. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2013.01.036. Epub 2013 Jan 29. FEBS Lett. 2013. PMID: 23376479 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular bases of viral RNA targeting by viral small interfering RNA-programmed RISC.J Virol. 2007 Apr;81(8):3797-806. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02383-06. Epub 2007 Jan 31. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17267504 Free PMC article.
-
Defective Interfering RNAs: Foes of Viruses and Friends of Virologists.Viruses. 2009 Dec;1(3):895-919. doi: 10.3390/v1030895. Epub 2009 Nov 10. Viruses. 2009. PMID: 21994575 Free PMC article.
-
A viral satellite RNA induces yellow symptoms on tobacco by targeting a gene involved in chlorophyll biosynthesis using the RNA silencing machinery.PLoS Pathog. 2011 May;7(5):e1002021. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002021. Epub 2011 May 5. PLoS Pathog. 2011. PMID: 21573143 Free PMC article.
-
RNAi-associated ssRNA-specific ribonucleases in Tombusvirus P19 mutant-infected plants and evidence for a discrete siRNA-containing effector complex.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Jan 30;104(5):1714-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0608117104. Epub 2007 Jan 23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 17244709 Free PMC article.
-
Transgenic resistance to Bamboo mosaic virus by expression of interfering satellite RNA.Mol Plant Pathol. 2013 Sep;14(7):693-707. doi: 10.1111/mpp.12040. Epub 2013 May 16. Mol Plant Pathol. 2013. PMID: 23675895 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chang, Y. C., M. Borja, H. B. Scholthof, A. O. Jackson, and T. J. Morris. 1995. Host effects and sequences essential for accumulation of defective interfering RNAs of cucumber necrosis and tomato bushy stunt tombusviruses. Virology 210:41-53. - PubMed
-
- Hamilton, A. J., and D. C. Baulcombe. 1999. A species of small antisense RNA in posttranscriptional gene silencing in plants. Science 286:950-952. - PubMed
-
- Hannon, G. J. 2002. RNA interference. Nature 418:244-251. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

