Initiation of translocation by Type I restriction-modification enzymes is associated with a short DNA extrusion
- PMID: 15598825
- PMCID: PMC545467
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkh999
Initiation of translocation by Type I restriction-modification enzymes is associated with a short DNA extrusion
Abstract
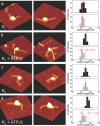
Recognition of 'foreign' DNA by Type I restriction-modification (R-M) enzymes elicits an ATP-dependent switch from methylase to endonuclease activity, which involves DNA translocation by the restriction subunit HsdR. Type I R-M enzymes are composed of three (Hsd) subunits with a stoichiometry of HsdR2:HsdM2:HsdS1 (R2-complex). However, the EcoR124I R-M enzyme can also exist as a cleavage deficient, sub-assembly of HsdR1:HsdM2:HsdS1 (R1-complex). ATPS was used to trap initial translocation complexes, which were visualized by Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM). In the R1-complex, a small bulge, associated with a shortening in the contour-length of the DNA of 8 nm, was observed. This bulge was found to be sensitive to single-strand DNA nucleases, indicative of non-duplexed DNA. R2-complexes appeared larger in the AFM images and the DNA contour length showed a shortening of approximately 11 nm, suggesting that two bulges were formed. Disclosure of the structure of the first stage after the recognition-translocation switch of Type I restriction enzymes forms an important first step in resolving a detailed mechanistic picture of DNA translocation by SF-II DNA translocation motors.
Figures




References
-
- Yuan R., Hamilton,D.L. and Burckhardt,J. (1980) DNA translocation by the restriction enzyme from E.coli K. Cell, 20, 237–244. - PubMed
-
- Endlich B. and Linn,S. (1985) The DNA restriction endonuclease of Escherichia coli B. I. Studies of the DNA translocation and the ATPase activities. J. Biol. Chem., 260, 5720–5728. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

