Targeted deletion of numb and numblike in sensory neurons reveals their essential functions in axon arborization
- PMID: 15598981
- PMCID: PMC540232
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1246005
Targeted deletion of numb and numblike in sensory neurons reveals their essential functions in axon arborization
Abstract
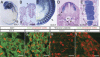
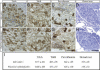
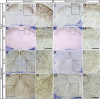
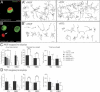
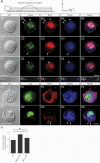
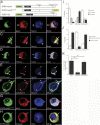
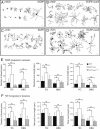
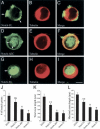
Mouse Numb homologs antagonize Notch1 signaling pathways through largely unknown mechanisms. Here we demonstrate that conditional mouse mutants with deletion of numb and numblike in developing sensory ganglia show a severe reduction in axonal arborization in afferent fibers, but no deficit in neurogenesis. Consistent with these results, expression of Cre recombinase in sensory neurons from numb conditional mutants results in reduced endocytosis, a significant increase in nuclear Notch1, and severe reductions in axon branch points and total axon length. Conversely, overexpression of Numb, but not mutant Numb lacking alpha-adaptin-interacting domain, leads to accumulation of Notch1 in markedly enlarged endocytic-lysosomal vesicles, reduced nuclear Notch1, and dramatic increases in axonal length and branch points. Taken together, our data provide evidence for previously unidentified functions of Numb and Numblike in sensory axon arborization by regulating Notch1 via the endocytic-lysosomal pathways.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Differential expression of mammalian Numb, Numblike and Notch1 suggests distinct roles during mouse cortical neurogenesis.Development. 1997 May;124(10):1887-97. doi: 10.1242/dev.124.10.1887. Development. 1997. PMID: 9169836
-
The Notch regulator Numb links the Notch and TCR signaling pathways.J Immunol. 2005 Jan 15;174(2):890-7. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.174.2.890. J Immunol. 2005. PMID: 15634911
-
Deletion of Numb/Numblike in glutamatergic neurons leads to anxiety-like behavior in mice.Brain Res. 2017 Jun 15;1665:36-49. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2017.02.025. Epub 2017 Mar 24. Brain Res. 2017. PMID: 28347671
-
Numb regulates post-endocytic trafficking and degradation of Notch1.J Biol Chem. 2009 Sep 25;284(39):26427-38. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.014845. Epub 2009 Jun 30. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19567869 Free PMC article.
-
Numb and Numblike control cell number during vertebrate neurogenesis.Trends Neurosci. 2003 Aug;26(8):395-6. doi: 10.1016/S0166-2236(03)00166-8. Trends Neurosci. 2003. PMID: 12900165 Review.
Cited by
-
Cleaved Delta like 1 intracellular domain regulates neural development via Notch signal-dependent and -independent pathways.Development. 2021 Oct 1;148(19):dev193664. doi: 10.1242/dev.193664. Epub 2021 Oct 4. Development. 2021. PMID: 34519339 Free PMC article.
-
Notch signalling in adult neurons: a potential target for microtubule stabilization.Ther Adv Neurol Disord. 2013 Nov;6(6):375-85. doi: 10.1177/1756285613490051. Ther Adv Neurol Disord. 2013. PMID: 24228073 Free PMC article.
-
Timing cell-fate determination during asymmetric cell divisions.Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2008 Oct;18(5):472-8. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2008.10.005. Epub 2008 Nov 12. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2008. PMID: 18983918 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Numb is not a critical regulator of Notch-mediated cell fate decisions in the developing chick inner ear.Front Cell Neurosci. 2015 Mar 12;9:74. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2015.00074. eCollection 2015. Front Cell Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25814931 Free PMC article.
-
Not(ch) just development: Notch signalling in the adult brain.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2011 May;12(5):269-83. doi: 10.1038/nrn3024. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21505516 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Anderson D.J. 1999. Lineages and transcription factors in the specification of vertebrate primary sensory neurons. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 9: 517–524. - PubMed
-
- Arber S., Ladle, D.R., Lin, J.H., Frank, E., and Jessell, T.M. 2000. ETS gene Er81 controls the formation of functional connections between group Ia sensory afferents and motor neurons. Cell 101: 485–498. - PubMed
-
- Berdnik D., Torok, T., Gonzalez-Gaitan, M., and Knoblich, J.A. 2002. The endocytic protein α-adaptin is required for numbmediated asymmetric cell division in Drosophila. Dev. Cell 3: 221–231. - PubMed
-
- Berezovska O., McLean, P., Knowles, R., Frosh, M., Lu, F.M., Lux, S.E., and Hyman, B.T. 1999. Notch1 inhibits neurite outgrowth in postmitotic primary neurons. Neuroscience 93: 433–439. - PubMed
-
- Berezovska O., Jack, P., McLean, C., Aster, J.C., Hicks, C., Xia, W., Wolfe, M.S., Kimberly, W.T., Weinmaster, G., Selkoe, D.J., et al. 2000. Aspartate mutations in presenilin and γ-secretase inhibitors both impair notch1 proteolysis and nuclear translocation with relative preservation of notch1 signaling. J. Neurochem. 75: 583–593. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
