Acid sensing in renal epithelial cells
- PMID: 15599393
- PMCID: PMC535075
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI23864
Acid sensing in renal epithelial cells
Abstract
The kidney adjusts net acid excretion to match production with exquisite precision, despite little or no change in the plasma bicarbonate concentration. The acid-sensing pathway that signals the kidney to increase acid secretion involves activation of the proto-oncogene c-Src. A new study in this issue shows that proline-rich tyrosine kinase 2 (Pyk2) is responsible for acid-induced activation of c-Src and is essential for acid sensing in renal epithelial cells. The findings implicate a broader role for Pyk2 in acid-base homeostasis in bone and other tissues beyond the kidney.
Figures
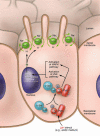
Comment on
-
Pyk2 activation is integral to acid stimulation of sodium/hydrogen exchanger 3.J Clin Invest. 2004 Dec;114(12):1782-9. doi: 10.1172/JCI18046. J Clin Invest. 2004. PMID: 15599403 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kurtz I, Maher T, Hulter HN, Schambelan M, Sebastian A. Effect of diet on plasma acid-base composition in normal humans. Kidney Int. 1983;24:670–680. - PubMed
-
- Nagami GT. Ammonia production and secretion by the proximal tubule. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 1989;14:258–261. - PubMed
-
- Hamm LL, Hering-Smith KS. Pathophysiology of hypocitraturic nephrolithiasis. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. North Am. 2002;31:885–893, viii. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

