Natural population dynamics and expansion of pathogenic clones of Staphylococcus aureus
- PMID: 15599398
- PMCID: PMC535072
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI23083
Natural population dynamics and expansion of pathogenic clones of Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
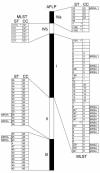
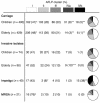
The population structure of Staphylococcus aureus carried by healthy humans was determined using a large strain collection of nonclinical origin (n = 829). High-throughput amplified fragment length polymorphism (AFLP) analysis revealed 3 major and 2 minor genetic clusters of S. aureus, which were corroborated by multilocus sequence typing. Major AFLP cluster I comprised 44.4% of the carriage isolates and showed additional heterogeneity whereas major AFLP groups II and III presented 2 homogeneous clusters, including 47.3% of all carriage isolates. Coanalysis of invasive S. aureus strains and epidemic methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) revealed that all major clusters contained invasive and multiresistant isolates. However, clusters and subclusters with overrepresentation of invasive isolates were also identified. Bacteremia in elderly adults, for instance, was caused by a IVa cluster-derived strain significantly more often than by strains from other AFLP clusters. Furthermore, expansion of multiresistant clones or clones associated with skin disease (impetigo) was detected, which suggests that epidemic potential is present in pathogenic strains of S. aureus. In addition, the virulence gene encoding Panton-Valentine leukocidin was significantly enriched in S. aureus strains causing abscesses and arthritis in comparison with the carriage group. We provide evidence that essentially any S. aureus genotype carried by humans can transform into a life-threatening human pathogen but that certain clones are more virulent than others.
Figures



Comment in
-
The Staphylococcus aureus "superbug".J Clin Invest. 2004 Dec;114(12):1693-6. doi: 10.1172/JCI23825. J Clin Invest. 2004. PMID: 15599392 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Steinberg JP, Clark CC, Hackman BO. Nosocomial and community-acquired Staphylococcus aureus bacteremias from 1980 to 1993: impact of intravascular devices and methicillin resistance. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1996;23:255–259. - PubMed
-
- Staphylococcus Laboratory, Statens Serum Institut. 2003. Annual report on Staphylococcus aureus bacteraemia cases 2001. Staphylococcus Laboratory, National Center for Antimicrobials and Infection Control, Statens Serum Institut. Copenhagen, Denmark. 9 pp.
-
- Luzar MA, et al. Staphylococcus aureus nasal carriage and infection in patients on continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis. N. Engl. J. Med. 1990;322:505–509. - PubMed
-
- Yu VL, et al. Staphylococcus aureus nasal carriage and infection in patients on hemodialysis. Efficacy of antibiotic prophylaxis. N. Engl. J. Med. 1986;315:91–96. - PubMed
-
- Nguyen MH, et al. Nasal carriage of and infection with Staphylococcus aureus in HIV-infected patients. Ann. Intern. Med. 1999;130:221–225. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

