Pyk2 activation is integral to acid stimulation of sodium/hydrogen exchanger 3
- PMID: 15599403
- PMCID: PMC535061
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI18046
Pyk2 activation is integral to acid stimulation of sodium/hydrogen exchanger 3
Abstract
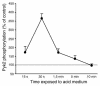
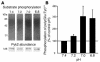
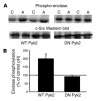
The present study examines the role of Pyk2 in acid regulation of sodium/hydrogen exchanger 3 (NHE3) activity in OKP cells, a kidney proximal tubule epithelial cell line. Incubation of OKP cells in acid media caused a transient increase in Pyk2 phosphorylation that peaked at 30 seconds and increased Pyk2/c-Src binding at 90 seconds. Pyk2 isolated by immunoprecipitation and studied in a cell-free system was activated and phosphorylated at acidic pH. Acid activation of Pyk2 (a) was specific for Pyk2 in that acid did not activate focal adhesion kinase, (b) required calcium, and (c) was associated with increased affinity for ATP. Transfection of OKP cells with dominant-negative pyk2(K457A) or small interfering pyk2 duplex RNA blocked acid activation of NHE3, while neither had an effect on glucocorticoid activation of NHE3. In addition, pyk2(K457A) blocked acid activation of c-Src kinase, which is also required for acid regulation of NHE3. The present results demonstrate that Pyk2 is directly activated by acidic pH and that Pyk2 activation is required for acid activation of c-Src kinase and NHE3. Given that partially purified Pyk2 can be activated by acid in a cell-free system, Pyk2 may serve as the pH sensor that initiates the acid-regulated signaling cascade involved in NHE3 regulation.
Figures
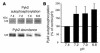
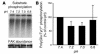
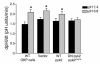
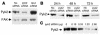
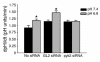

Comment in
-
Acid sensing in renal epithelial cells.J Clin Invest. 2004 Dec;114(12):1696-9. doi: 10.1172/JCI23864. J Clin Invest. 2004. PMID: 15599393 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alpern RJ, Sakhaee K. The clinical spectrum of chronic metabolic acidosis: homeostatic mechanisms produce significant morbidity. Am. J. Kid. Dis. 1997;29:291–302. - PubMed
-
- Tsuganezawa H, et al. Role of c-Src and ERK in acid-induced activation of NHE3. Kidney Int. 2002;62:41–50. - PubMed
-
- Yamaji Y, Tsuganezawa H, Moe OW, Alpern RJ. Intracellular acidosis activates c-Src. Am. J. Physiol. 1997;272:C886–C893. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

