Cofolding organizes alfalfa mosaic virus RNA and coat protein for replication
- PMID: 15604410
- PMCID: PMC1500904
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1103399
Cofolding organizes alfalfa mosaic virus RNA and coat protein for replication
Abstract
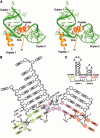
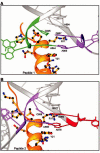
Alfalfa mosaic virus genomic RNAs are infectious only when the viral coat protein binds to the RNA 3' termini. The crystal structure of an alfalfa mosaic virus RNA-peptide complex reveals that conserved AUGC repeats and Pro-Thr-x-Arg-Ser-x-x-Tyr coat protein amino acids cofold upon interacting. Alternating AUGC residues have opposite orientation, and they base pair in different adjacent duplexes. Localized RNA backbone reversals stabilized by arginine-guanine interactions place the adenosines and guanines in reverse order in the duplex. The results suggest that a uniform, organized 3' conformation, similar to that found on viral RNAs with transfer RNA-like ends, may be essential for replication.
Figures

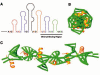
Similar articles
-
Base-pairing potential identified by in vitro selection predicts the kinked RNA backbone observed in the crystal structure of the alfalfa mosaic virus RNA-coat protein complex.J Mol Recognit. 2006 Jan-Feb;19(1):68-78. doi: 10.1002/jmr.759. J Mol Recognit. 2006. PMID: 16312015
-
Degenerate in vitro genetic selection reveals mutations that diminish alfalfa mosaic virus RNA replication without affecting coat protein binding.J Virol. 2004 Aug;78(15):8036-46. doi: 10.1128/JVI.78.15.8036-8046.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 15254175 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro genetic selection analysis of alfalfa mosaic virus coat protein binding to 3'-terminal AUGC repeats in the viral RNAs.J Virol. 1997 Mar;71(3):2310-9. doi: 10.1128/JVI.71.3.2310-2319.1997. J Virol. 1997. PMID: 9032367 Free PMC article.
-
Alfalfa mosaic virus and ilarviruses: involvement of coat protein in multiple steps of the replication cycle.J Gen Virol. 1999 May;80 ( Pt 5):1089-1102. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-80-5-1089. J Gen Virol. 1999. PMID: 10355754 Review. No abstract available.
-
RNA-protein interactions in spherical viruses.Arch Virol. 2002 Dec;147(12):2261-79. doi: 10.1007/s00705-002-0891-6. Arch Virol. 2002. PMID: 12491096 Review.
Cited by
-
Coat protein activation of alfalfa mosaic virus replication is concentration dependent.J Virol. 2005 May;79(9):5752-61. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.9.5752-5761.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 15827190 Free PMC article.
-
Non-canonical Translation in Plant RNA Viruses.Front Plant Sci. 2017 Apr 6;8:494. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2017.00494. eCollection 2017. Front Plant Sci. 2017. PMID: 28428795 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of the conformational switch model for alfalfa mosaic virus RNA replication.J Virol. 2005 May;79(9):5743-51. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.9.5743-5751.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 15827189 Free PMC article.
-
Deep structural insights into RNA-binding disordered protein regions.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2022 Sep;13(5):e1714. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1714. Epub 2022 Jan 30. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2022. PMID: 35098694 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cytoplasmic granule formation and translational inhibition of nodaviral RNAs in the absence of the double-stranded RNA binding protein B2.J Virol. 2013 Dec;87(24):13409-21. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02362-13. Epub 2013 Oct 2. J Virol. 2013. PMID: 24089564 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

