Exercise physiology versus inactivity physiology: an essential concept for understanding lipoprotein lipase regulation
- PMID: 15604935
- PMCID: PMC4312662
- DOI: 10.1097/00003677-200410000-00007
Exercise physiology versus inactivity physiology: an essential concept for understanding lipoprotein lipase regulation
Abstract
Some health-related proteins such as lipoprotein lipase may be regulated by qualitatively different processes over the physical activity continuum, sometimes with very high sensitivity to inactivity. The most powerful process known to regulate lipoprotein lipase protein and activity in muscle capillaries may be initiated by inhibitory signals during physical inactivity, independent of changes in lipoprotein lipase messenger RNA.
Figures
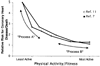
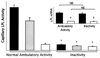
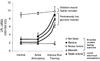
 ; N = 7), and fast-twitch white quadriceps muscle sections least recruited (□; N = 6) during ambulatory activity (2). *P < 0.05 indicates significant difference between reduced activity and ambulatory activity. †P < 0.05 indicates significantly lower LPL mRNA in fast-twitch white muscle than in red oxidative soleus muscle. NS, no significant difference in LPL mRNA between inactivity and ambulatory activity measured by Northern blotting (2) and by real-time polymerase chain reaction (3).
; N = 7), and fast-twitch white quadriceps muscle sections least recruited (□; N = 6) during ambulatory activity (2). *P < 0.05 indicates significant difference between reduced activity and ambulatory activity. †P < 0.05 indicates significantly lower LPL mRNA in fast-twitch white muscle than in red oxidative soleus muscle. NS, no significant difference in LPL mRNA between inactivity and ambulatory activity measured by Northern blotting (2) and by real-time polymerase chain reaction (3).

References
-
- Bey L, Areiqat E, Sano A, Hamilton MT. Reduced lipoprotein lipase activity in postural skeletal muscle during aging. J. Appl. Physiol. 2001;91:687–692. - PubMed
-
- Bey L, Akunuri N, Zhao P, Hoffman EP, Hamilton DG, Hamilton MT. Patterns of global gene expression in rat skeletal muscle during unloading and low-intensity ambulatory activity. Physiol. Genomics. 2003;13:157–167. - PubMed
-
- Fan J, Unoki H, Kojima N, Sun H, Shimoyamada H, Deng H, Okazaki M, Shikama H, Yamada N, Watanabe T. Overexpression of lipoprotein lipase in transgenic rabbits inhibits diet-induced hypercholesterolemia and atherosclerosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2001;276:40071–40079. - PubMed
-
- Hamilton MT, Etienne J, McClure WC, Pavey BS, Holloway AK. Role of local contractile activity and muscle fiber type on LPL regulation during exercise. Am. J. Physiol. 1998;275:E1016–E1022. - PubMed

