Lornoxicam pharmacokinetics in relation to cytochrome P450 2C9 genotype
- PMID: 15606435
- PMCID: PMC1884973
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2005.02223.x
Lornoxicam pharmacokinetics in relation to cytochrome P450 2C9 genotype
Abstract
Aims: To investigate the pharmacokinetics of lornoxicam and the relationship with CYP2C9 polymorphism in healthy Chinese subjects.
Methods: A single oral dose of 8 mg lornoxicam was administered to 18 healthy Chinese male subjects. Plasma was sampled for 24 h post dose, and plasma concentrations of lornoxicam were measured using a validated LC/MS/MS method. CYP2C9 genotype was determined by polymerase chain reaction-based restriction fragment length polymorphism or by direct sequencing of the coding region of the CYP2C9 gene.
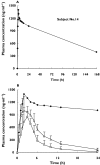
Results: Of the 18 subjects, one subject was found to be a very poor metabolizer of lornoxicam with a long t(1/2) of 106 h, a low CL/F of 0.71 ml min(-1), and a high AUC(0-infinity) of 187.6 microg ml(-1) h. Genotyping studies revealed that this subject was heterozygous for CYP2C9*3 and a new variant CYP2C9 allele. Of the other 17 subjects, 13 were *1/*1 carriers, three were *1/*3 carriers, and one was a *1/*2 carrier. Mean AUC(0-infinity) values (95% confidence intervals) of lornoxicam were 9.25 (6.55, 11.95) vs. 4.75 (3.55, 5.95) microg ml(-1) h in *1 heterozygotes vs.*1 homozygotes, and mean CL/F values were 14.8 (10.2, 19.4) vs. 32.9 (24.5, 41.3) ml min(-1), respectively (P < 0.05 for both AUC and CL/F).
Conclusions: The results show that the pharmacokinetics of lornoxicam are dependent on CYP2C9 polymorphism. In particular, the presence of the CYP2C9*3 allele impairs the oral clearance of lornoxicam.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Impact of cytochrome P450 CYP2C9 variant allele CYP2C9 * 3 on the pharmacokinetics of glibenclamide and lornoxicam in Chinese subjects].Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2005 Sep;40(9):796-9. Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2005. PMID: 16342679 Chinese.
-
Effect of the CYP2C9*3 allele on lornoxicam metabolism.Clin Chim Acta. 2006 Feb;364(1-2):287-91. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2005.07.013. Epub 2005 Sep 22. Clin Chim Acta. 2006. PMID: 16182270
-
CYP2C9 genotypes and the pharmacokinetics of tenoxicam in Brazilians.Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2004 Jul;76(1):18-26. doi: 10.1016/j.clpt.2004.03.002. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2004. PMID: 15229460
-
Clinical consequences of cytochrome P450 2C9 polymorphisms.Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2005 Jan;77(1):1-16. doi: 10.1016/j.clpt.2004.08.009. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2005. PMID: 15637526 Review.
-
Genetically based impairment in CYP2C8- and CYP2C9-dependent NSAID metabolism as a risk factor for gastrointestinal bleeding: is a combination of pharmacogenomics and metabolomics required to improve personalized medicine?Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2009 Jun;5(6):607-20. doi: 10.1517/17425250902970998. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2009. PMID: 19422321 Review.
Cited by
-
Matrix-mini-tablets of lornoxicam for targeting early morning peak symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2014 May;17(5):357-69. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2014. PMID: 24967065 Free PMC article.
-
Niosome as a promising tool for increasing the effectiveness of anti-inflammatory compounds.EXCLI J. 2024 Feb 7;23:212-263. doi: 10.17179/excli2023-6868. eCollection 2024. EXCLI J. 2024. PMID: 38487088 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunomodulatory Effects of the Cyclooxygenase Inhibitor Lornoxicam on Phenotype and Function of Camel Blood Leukocytes.Animals (Basel). 2021 Jul 6;11(7):2023. doi: 10.3390/ani11072023. Animals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34359151 Free PMC article.
-
Niosomal gel of lornoxicam for topical delivery: in vitro assessment and pharmacodynamic activity.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2013 Sep;14(3):1072-82. doi: 10.1208/s12249-013-9986-5. Epub 2013 Jul 2. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2013. PMID: 23818079 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of CYP2C9 and CYP2C19 genetic polymorphisms on pharmacokinetics of gliclazide MR in Chinese subjects.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2007 Jul;64(1):67-74. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2007.02846.x. Epub 2007 Feb 12. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17298483 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Skjodt NM, Davies NM. Clinical pharmacokinetics of lornoxicam, a short half-life oxicam. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1998;34:421–8. - PubMed
-
- Bonnabry P, Leemann T, Dayer P. Role of human liver microsomal CYP2C9 in the biotransformation of lornoxicam. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1996;49:305–8. - PubMed
-
- Jun I, Ichiro I, Kohsuke M, et al. Polymorphism of the cytochrome P450 (CYP) 2C9 gene in Japanese epileptic patients: genetic analysis of the CYP2C9 locus. Pharmacogenetics. 2000;10:85–9. - PubMed
-
- Dickmann LJ, Rettie AE, Kneller MB, et al. Identification and functional characterization of a new CYP2C9 variant (CYP2C9*51) expressed among African Americans. Mol Pharmacol. 2001;60:382–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous