Vaccination of neonatal calves with Mycobacterium bovis BCG induces protection against intranasal challenge with virulent M. bovis
- PMID: 15606613
- PMCID: PMC1809274
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2005.02668.x
Vaccination of neonatal calves with Mycobacterium bovis BCG induces protection against intranasal challenge with virulent M. bovis
Erratum in
- Clin Exp Immunol. 2005 Apr;140(1):192
Abstract
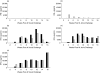
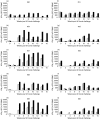
Vaccination of neonates with Mycobacterium bovis bacillus Calmette-Guerin (BCG) may be a strategy that overcomes reduced vaccine efficacy associated with exposure to environmental mycobacteria in humans and cattle. Preliminary comparisons indicated that 2-week-old calves produced an immune response to vaccination at least as intense as that observed in adults. Subsequently, five gnotobiotic hysterotomy derived calves aged 1 day were inoculated with BCG and 3 months later were challenged intranasally with virulent M. bovis. The number of tissues with lesions and the pathological extent of these lesions was reduced significantly in vaccinates. Furthermore, lesions were evident in the lung or associated chest lymph nodes of four of five controls but none of five vaccinates. BCG vaccination reduced significantly the level of bacterial colonization. However, lesions in the head associated lymph nodes were observed in three of five BCG-vaccinated cattle. Levels of interferon gamma (IFN-gamma) detected by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) or enzyme-linked immunospot (ELISPOT) in individual vaccinated animals at challenge did not correlate with subsequent resistance and in general immune responses post-challenge were lower in vaccinated calves. Low IL-10 responses were evident but IL-4 was not detected. Responses to ESAT-6 and/or CFP-10 were evident in four of four control calves that had lesions. Two of the BCG vaccinates with lesions did not produce a response to ESAT-6 and CFP-10, indicating that these antigens did not distinguish vaccinated immune animals from vaccinated animals with lesions. Overall, vaccination of neonatal calves with BCG induced significant protection against disease and has potential as a strategy for the reduction of the incidence of bovine tuberculosis.
Figures

References
-
- Colditz GA, Berkey CS, Mosteller F, et al. The efficacy of bacillus Calmette–Guérin vaccination of newborns and infants in the prevention of tuberculosis: meta-analyses of the published literature. Pediatrics. 1995;96:29–35. - PubMed
-
- Fine PE. Variation in protection by BCG: implications of and for heterologous immunity. Lancet. 1995;346:1339–45. - PubMed
-
- Palmer CE, Long MW. Effects of infection with atypical mycobacteria on BCG vaccination and tuberculosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1966;94:553–68. - PubMed
-
- Black GF, Dockrell HM, Crampin AC, et al. Patterns and implications of naturally acquired immune responses to environmental and tuberculous mycobacterial antigens in northern Malawi. J Infect Dis. 2001;184:322–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

