Role of p38 MAPK and NF-kB for chemokine release in coculture of human eosinophils and bronchial epithelial cells
- PMID: 15606618
- PMCID: PMC1809270
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2005.02678.x
Role of p38 MAPK and NF-kB for chemokine release in coculture of human eosinophils and bronchial epithelial cells
Abstract
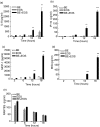
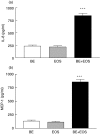
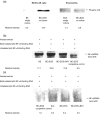
Eosinophils are principal effector cells of inflammation in allergic asthma, characterized by their accumulation and infiltration at inflammatory sites mediated by the chemokine eotaxin and their interaction with adhesion molecules expressed on bronchial epithelial cells. We investigated the modulation of nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB) and the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway on the in vitro release of chemokines including regulated upon activation normal T cell expressed and secreted (RANTES), monokine induced by interferon-gamma (MIG), monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1), interleukin (IL)-8, and interferon-inducible protein-10 (IP-10) upon the interaction of human bronchial epithelial BEAS-2B cells and eosinophils. Gene expression of chemokines was evaluated by RT-PCR and the induction amount of chemokines quantified by cytometric bead array. NF-kappaB and p38 MAPK activities were assessed by electrophoretic mobility shift assay and Western blot, respectively. The interaction of eosinophils and BEAS-2B cells was found to up-regulate the gene expression of the chemokines IL-8, MCP-1, MIG, RANTES and IP-10 expression in BEAS-2B cells, and to significantly elevate the release of the aforementioned chemokines except RANTES in a coculture of BEAS-2B cells and eosinophils. IkappaB-alpha phosphorylation inhibitor, BAY 11-7082, and p38 MAPK inhibitor, SB 203580 could decrease the release of IL-8, IP-10 and MCP-1 in the coculture. Together, the above results show that the induction of the release of chemokines in a coculture of epithelial cells and eosinophils are regulated by p38 MAPK and NF-kappaB activities of BEAS-2B cells, at least partly, through intercellular contact. Our findings therefore shed light on the future development of more effective agents for allergic and inflammatory diseases.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Induction of IL-6 in co-culture of bronchial epithelial cells and eosinophils is regulated by p38 MAPK and NF-kappaB.Allergy. 2005 Nov;60(11):1378-85. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.2005.00884.x. Allergy. 2005. PMID: 16197469
-
House dust mite allergen Der p 1 elevates the release of inflammatory cytokines and expression of adhesion molecules in co-culture of human eosinophils and bronchial epithelial cells.Int Immunol. 2006 Aug;18(8):1327-35. doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxl065. Epub 2006 Jun 23. Int Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16798840
-
Interleukin-25-induced chemokines and interleukin-6 release from eosinophils is mediated by p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase, c-Jun N-terminal kinase, and nuclear factor-kappaB.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2005 Aug;33(2):186-94. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2005-0034OC. Epub 2005 Apr 28. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2005. PMID: 15860795
-
Induction of adhesion molecules upon the interaction between eosinophils and bronchial epithelial cells: involvement of p38 MAPK and NF-kappaB.Int Immunopharmacol. 2006 Dec 5;6(12):1859-71. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2006.08.003. Epub 2006 Sep 1. Int Immunopharmacol. 2006. PMID: 17052676
-
Nf-kappa B, chemokine gene transcription and tumour growth.Nat Rev Immunol. 2002 Sep;2(9):664-74. doi: 10.1038/nri887. Nat Rev Immunol. 2002. PMID: 12209135 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Carbon monoxide-releasing molecule-2 suppresses thrombomodulin and endothelial protein C receptor expression of human umbilical vein endothelial cells induced by lipopolysaccharide in vitro.Medicine (Baltimore). 2017 May;96(21):e6978. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000006978. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017. PMID: 28538400 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-inflammatory effects of exendin-4, a glucagon-like peptide-1 analog, on human peripheral lymphocytes in patients with type 2 diabetes.J Diabetes Investig. 2013 Jul 8;4(4):382-92. doi: 10.1111/jdi.12063. Epub 2013 Apr 18. J Diabetes Investig. 2013. PMID: 24843684 Free PMC article.
-
NOD-like receptors mediated activation of eosinophils interacting with bronchial epithelial cells: a link between innate immunity and allergic asthma.Cell Mol Immunol. 2013 Jul;10(4):317-29. doi: 10.1038/cmi.2012.77. Epub 2013 Mar 25. Cell Mol Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23524653 Free PMC article.
-
CDKN2A Deletion in Melanoma Excludes T Cell Infiltration by Repressing Chemokine Expression in a Cell Cycle-Dependent Manner.Front Oncol. 2021 Mar 25;11:641077. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.641077. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33842347 Free PMC article.
-
FNF-12, a novel benzylidene-chromanone derivative, attenuates inflammatory response in in vitro and in vivo asthma models mediated by M2-related Th2 cytokines via MAPK and NF-kB signaling.Pharmacol Rep. 2022 Feb;74(1):96-110. doi: 10.1007/s43440-021-00325-0. Epub 2021 Sep 1. Pharmacol Rep. 2022. PMID: 34468975
References
-
- Chiappara G, Gagliardo R, Siena A, et al. Airway remodelling in the pathogenesis of asthma. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2001;1:85–93. - PubMed
-
- Walsh GM. Eosinophil–epithelial cell interactions: a special relationship? Clin Exp Allergy. 2001;31:351–4. - PubMed
-
- Walsh GM. Eosinophil granule proteins and their role in disease. Curr Opin Hematol. 2001;8:28–33. - PubMed
-
- Giembycz MA, Lindsay MA. Pharmacology of the eosinophil. Pharmacol Rev. 1999;51:213–340. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

