Directed evolution of single-chain Fv for cytoplasmic expression using the beta-galactosidase complementation assay results in proteins highly susceptible to protease degradation and aggregation
- PMID: 15606918
- PMCID: PMC544847
- DOI: 10.1186/1475-2859-3-16
Directed evolution of single-chain Fv for cytoplasmic expression using the beta-galactosidase complementation assay results in proteins highly susceptible to protease degradation and aggregation
Abstract
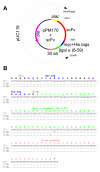
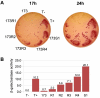
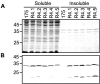
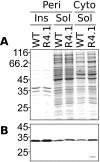
BACKGROUND: Antibody fragments are molecules widely used for diagnosis and therapy. A large amount of protein is frequently required for such applications. New approaches using folding reporter enzymes have recently been proposed to increase soluble expression of foreign proteins in Escherichia coli. To date, these methods have only been used to screen for proteins with better folding properties but have never been used to select from a large library of mutants. In this paper we apply one of these methods to select mutations that increase the soluble expression of two antibody fragments in the cytoplasm of E. coli. RESULTS: We used the beta-galactosidase alpha-complementation system to monitor and evolve two antibody fragments for high expression levels in E. coli cytoplasm. After four rounds of mutagenesis and selection from large library repertoires (>107 clones), clones exhibiting high levels of beta-galactosidase activity were isolated. These clones expressed a higher amount of soluble fusion protein than the wild type in the cytoplasm, particularly in a strain deficient in the cytoplasmic Lon protease. The increase in the soluble expression level of the unfused scFv was, however, much less pronounced, and the unfused proteins proved to be more aggregation prone than the wild type. In addition, the soluble expression levels were not correlated with the beta-galactosidase activity present in the cells. CONCLUSION: This is the first report of a selection for soluble protein expression using a fusion reporter method. Contrary to anticipated results, high enzymatic activity did not correlate with the soluble protein expression level. This was presumably due to free alpha-peptide released from the protein fusion by the host proteases. This means that the alpha-complementation assay does not sense the fusion expression level, as hypothesized, but rather the amount of free released alpha-peptide. Thus, the system does not select, in our case, for higher soluble protein expression level but rather for higher protease susceptibility of the fusion protein.
Figures


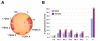



Similar articles
-
[Cloning and expression of human single-chain Fv antibody against amyloid beta peptide involved in Alzheimer's disease].Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2003 Oct;25(5):557-62. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2003. PMID: 14650158 Chinese.
-
Expression of an antibody fragment at high levels in the bacterial cytoplasm.J Mol Biol. 1998 Jul 3;280(1):117-27. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1998.1840. J Mol Biol. 1998. PMID: 9653035
-
[Cloning and expression of human single-chain Fv antibody against A beta(1-42) peptide involved in Alzheimer disease].Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi. 2008 Jun;37(6):400-4. Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi. 2008. PMID: 19031720 Chinese.
-
Expression of foreign proteins in Escherichia coli by fusing with an archaeal FK506 binding protein.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2004 Mar;64(1):99-105. doi: 10.1007/s00253-003-1459-4. Epub 2003 Oct 15. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2004. PMID: 14564491
-
Purification of secreted recombinant proteins from Escherichia coli.Bioprocess Technol. 1991;12:163-81. Bioprocess Technol. 1991. PMID: 1367083 Review.
Cited by
-
A rapid protein folding assay for the bacterial periplasm.Protein Sci. 2010 May;19(5):1079-90. doi: 10.1002/pro.388. Protein Sci. 2010. PMID: 20440843 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic selection for protein solubility enabled by the folding quality control feature of the twin-arginine translocation pathway.Protein Sci. 2006 Mar;15(3):449-58. doi: 10.1110/ps.051902606. Epub 2006 Feb 1. Protein Sci. 2006. PMID: 16452624 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of three putative Lon proteases of Thermus thermophilus HB27 and use of their defective mutants as hosts for production of heterologous proteins.Extremophiles. 2008 Mar;12(2):285-96. doi: 10.1007/s00792-007-0129-3. Epub 2007 Dec 22. Extremophiles. 2008. PMID: 18157502
-
Efficient isolation of soluble intracellular single-chain antibodies using the twin-arginine translocation machinery.J Mol Biol. 2009 Jan 9;385(1):299-311. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2008.10.051. Epub 2008 Nov 1. J Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 18992254 Free PMC article.
-
SAS: Split antibiotic selection for identifying chaperones that improve protein solubility.Heliyon. 2024 Mar 1;10(5):e26996. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e26996. eCollection 2024 Mar 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38495176 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Glockshuber R, Schmidt T, Pluckthun A. The disulfide bonds in antibody variable domains: effects on stability, folding in vitro, and functional expression in Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1992;31:1270–9. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

