3did: interacting protein domains of known three-dimensional structure
- PMID: 15608228
- PMCID: PMC539991
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gki037
3did: interacting protein domains of known three-dimensional structure
Abstract
The database of 3D Interacting Domains (3did) is a collection of domain-domain interactions in proteins for which high-resolution three-dimensional structures are known. 3did exploits structural information to provide critical molecular details necessary for understanding how interactions occur. It also offers an overview of how similar in structure are interactions between different members of the same protein family. The database also contains Gene Ontology-based functional annotations and interactions between yeast proteins from large-scale interaction discovery studies. A web-based tool to query 3did is available at http://3did.embl.de.
Figures
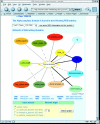

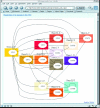
References
-
- Uetz P., Giot,L., Cagney,G., Mansfield,T.A., Judson,R.S., Knight,J.R., Lockshon,D., Narayan,V., Srinivasan,M., Pochart,P. et al. (2000) A comprehensive analysis of protein–protein interactions in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nature, 403, 623–627. - PubMed
-
- Rain J.C., Selig,L., De Reuse,H., Battaglia,V., Reverdy,C., Simon,S., Lenzen,G., Petel,F., Wojcik,J., Schachter,V. et al. (2001) The protein–protein interaction map of Helicobacter pylori. Nature, 409, 211–215. - PubMed
-
- Giot L., Bader,J.S., Brouwer,C., Chaudhuri,A., Kuang,B., Li,Y., Hao,Y.L., Ooi,C.E., Godwin,B., Vitols,E. et al. (2003) A protein interaction map of Drosophila melanogaster. Science, 302, 1727–1736. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

