The Vertebrate Genome Annotation (Vega) database
- PMID: 15608237
- PMCID: PMC540089
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gki135
The Vertebrate Genome Annotation (Vega) database
Abstract
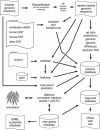
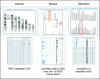
The Vertebrate Genome Annotation (Vega) database (http://vega.sanger.ac.uk) has been designed to be a community resource for browsing manual annotation of finished sequences from a variety of vertebrate genomes. Its core database is based on an Ensembl-style schema, extended to incorporate curation-specific metadata. In collaboration with the genome sequencing centres, Vega attempts to present consistent high-quality annotation of the published human chromosome sequences. In addition, it is also possible to view various finished regions from other vertebrates, including mouse and zebrafish. Vega displays only manually annotated gene structures built using transcriptional evidence, which can be examined in the browser. Attempts have been made to standardize the annotation procedure across each vertebrate genome, which should aid comparative analysis of orthologues across the different finished regions.
Figures


References
-
- Dunham I., Shimizu,N., Roe,B.A., Chissoe,S., Hunt,A.R., Collins,J.E., Bruskiewich,R., Beare,D.M., Clamp,M., Smink,L.J. et al. (1999) The DNA sequence of human chromosome 22. Nature, 402, 489–495. - PubMed
-
- Lander E.S., Linton,L.M., Birren,B., Nusbaum,C., Zody,M.C., Baldwin,J., Devon,K., Dewar,K., Doyle,M., FitzHugh,W. et al. (2001) Initial sequencing and analysis of the human genome. Nature, 409, 860–921. - PubMed
-
- Mallon A.-M., Wilming,L., Weekes,J., Gilbert,J.G.R., Ashurst,J., Peyrefitte,S., Matthews,L., Cadman,M., McKeone,R., Sellick,C.A. et al. (2004) Organization and evolution of a gene-rich region of the mouse genome: A 12.7-Mb region deleted in the Del(13)Svea36H mouse. Genome Res., 14, 1888–1901. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

