TRACTOR_DB: a database of regulatory networks in gamma-proteobacterial genomes
- PMID: 15608293
- PMCID: PMC540008
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gki054
TRACTOR_DB: a database of regulatory networks in gamma-proteobacterial genomes
Abstract
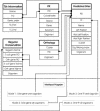
Experimental data on the Escherichia coli transcriptional regulatory system has been used in the past years to predict new regulatory elements (promoters, transcription factors (TFs), TFs' binding sites and operons) within its genome. As more genomes of gamma-proteobacteria are being sequenced, the prediction of these elements in a growing number of organisms has become more feasible, as a step towards the study of how different bacteria respond to environmental changes at the level of transcriptional regulation. In this work, we present TRACTOR_DB (TRAnscription FaCTORs' predicted binding sites in prokaryotic genomes), a relational database that contains computational predictions of new members of 74 regulons in 17 gamma-proteobacterial genomes. For these predictions we used a comparative genomics approach regarding which several proof-of-principle articles for large regulons have been published. TRACTOR_DB may be currently accessed at http://www.bioinfo.cu/Tractor_DB, http://www.tractor.lncc.br/ or at http://www.cifn.unam.mx/Computational_Genomics/tractorDB. Contact Email id is tractor@cifn.unam.mx.
Figures
References
-
- Cases I., de Lorenzo,V. and Ouzounis,C.A. (2003) Transcription regulation and environmental adaptation in bacteria. Trends Microbiol., 11, 248–253. - PubMed
-
- Thieffry D., Huerta,A.M., Pérez-Rueda,E. and Collado-Vides,J. (1998) From specific gene regulation to genomics networks: a global analysis of transcriptional regulation in Escherichia coli. Bioessays, 20, 433–440. - PubMed
-
- Hertz G.Z. and Stormo,G.D. (1999) Identifying DNA and protein patterns with statistically significant alignments of multiple sequences. Bioinformatics, 15, 563–577. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous