Identifying estrogen receptor alpha target genes using integrated computational genomics and chromatin immunoprecipitation microarray
- PMID: 15608294
- PMCID: PMC545447
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkh1005
Identifying estrogen receptor alpha target genes using integrated computational genomics and chromatin immunoprecipitation microarray
Abstract
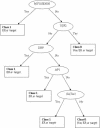
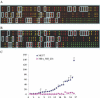
The estrogen receptor alpha (ERalpha) regulates gene expression by either direct binding to estrogen response elements or indirect tethering to other transcription factors on promoter targets. To identify these promoter sequences, we conducted a genome-wide screening with a novel microarray technique called ChIP-on-chip. A set of 70 candidate ERalpha loci were identified and the corresponding promoter sequences were analyzed by statistical pattern recognition and comparative genomics approaches. We found mouse counterparts for 63 of these loci and classified 42 (67%) as direct ERalpha targets using classification and regression tree (CART) statistical model, which involves position weight matrix and human-mouse sequence similarity scores as model parameters. The remaining genes were considered to be indirect targets. To validate this computational prediction, we conducted an additional ChIP-on-chip assay that identified acetylated chromatin components in active ERalpha promoters. Of the 27 loci upregulated in an ERalpha-positive breast cancer cell line, 20 having mouse counterparts were correctly predicted by CART. This integrated approach, therefore, sets a paradigm in which the iterative process of model refinement and experimental verification will continue until an accurate prediction of promoter target sequences is derived.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Genomic analyses of transcription factor binding, histone acetylation, and gene expression reveal mechanistically distinct classes of estrogen-regulated promoters.Mol Cell Biol. 2007 Jul;27(14):5090-104. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00083-07. Epub 2007 May 21. Mol Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17515612 Free PMC article.
-
Novel estrogen receptor-alpha binding sites and estradiol target genes identified by chromatin immunoprecipitation cloning in breast cancer.Cancer Res. 2007 May 15;67(10):5017-24. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-3696. Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17510434
-
Inference of hierarchical regulatory network of estrogen-dependent breast cancer through ChIP-based data.BMC Syst Biol. 2010 Dec 17;4:170. doi: 10.1186/1752-0509-4-170. BMC Syst Biol. 2010. PMID: 21167036 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic studies of transcription factor-DNA interactions.Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2005 Feb;9(1):38-45. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2004.12.008. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2005. PMID: 15701451 Review.
-
The first decade of estrogen receptor cistromics in breast cancer.J Endocrinol. 2016 May;229(2):R43-56. doi: 10.1530/JOE-16-0003. Epub 2016 Feb 23. J Endocrinol. 2016. PMID: 26906743 Review.
Cited by
-
Position weight matrix, gibbs sampler, and the associated significance tests in motif characterization and prediction.Scientifica (Cairo). 2012;2012:917540. doi: 10.6064/2012/917540. Epub 2012 Oct 23. Scientifica (Cairo). 2012. PMID: 24278755 Free PMC article. Review.
-
COTRASIF: conservation-aided transcription-factor-binding site finder.Nucleic Acids Res. 2009 Apr;37(7):e49. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkp084. Epub 2009 Mar 5. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009. PMID: 19264796 Free PMC article.
-
ER and PR signaling nodes during mammary gland development.Breast Cancer Res. 2012 Jul 19;14(4):210. doi: 10.1186/bcr3166. Breast Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22809143 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural and functional characterization of aromatase, estrogen receptor, and their genes in endocrine-responsive and -resistant breast cancer cells.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2016 Jul;161:73-83. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2015.07.018. Epub 2015 Aug 13. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 26277097 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome-wide approaches for identification of nuclear receptor target genes.Nucl Recept Signal. 2006;4:e018. doi: 10.1621/nrs.04018. Epub 2006 Jul 7. Nucl Recept Signal. 2006. PMID: 16862224 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kun Y., How,L.C., Hoon,T.P., Bajic,V.B., Lam,T.S., Aggarwal,A., Sze,H.G., Bok,W.S., Yin,W.C. and Tan,P. (2003) Classifying the estrogen receptor status of breast cancers by expression profiles reveals a poor prognosis subpopulation exhibiting high expression of the ERBB2 receptor. Hum. Mol. Genet., 12, 3245–3258. - PubMed
-
- Klinge C.M. (2000) Estrogen receptor interaction with co-activators and co-repressors. Steroids, 65, 227–251. - PubMed
-
- Abdelrahim A., Samudio,I., Smith,R., III, Burghardt,R. and Safe,S. (2002) Small inhibitory RNA duplexes for Sp1 mRNA block basal and estrogen-induced gene expression and cell cycle progression in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. J. Biol. Chem., 277, 28815–28822. - PubMed
-
- Gaub M.P., Bellard,M., Scheuer,I., Chambon,P. and Sassone-Corsi,P. (1990) Activation of the ovalbumin gene by the estrogen receptor involves the fos-jun complex. Cell, 63, 1267–1276. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

