Expression of cutaneous lymphocyte-associated antigen and E-selectin ligand by circulating human memory CD4+ T lymphocytes specific for herpes simplex virus type 2
- PMID: 15609235
- PMCID: PMC1255909
- DOI: 10.1086/426944
Expression of cutaneous lymphocyte-associated antigen and E-selectin ligand by circulating human memory CD4+ T lymphocytes specific for herpes simplex virus type 2
Abstract
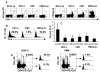
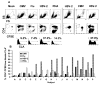
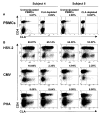
Virus-specific memory T lymphocytes traffic to sites of viral infection. Herpes simplex virus (HSV) type 2-specific CD4(+) and CD8(+) T lymphocytes differ with regard to their homing kinetics to infected tissues. We studied the expression of cutaneous lymphocyte-associated antigen (CLA) and E-selectin ligand (ESL) by HSV-2-specific CD4(+) T lymphocytes. Virus-reactive T lymphocytes were identified ex vivo by CD154 or interferon-gamma up-regulation. We detected selective expression of CLA by HSV-2-reactive CD4(+) T lymphocytes, but at levels lower than those we previously observed for CD8(+) T lymphocytes. Short-term HSV-2-reactive CD4(+) lines generated from peripheral-blood mononuclear cells preferentially express CLA, compared with cytomegalovirus- or influenza-specific cells. CLA is expressed by HSV-2-reactive cells that are initially CLA negative before restimulation. Short-term culture-expanded HSV-2-specific CD4(+) T lymphocytes also selectively express ESL. These findings have implications for the optimization of vaccines for HSV and other cutaneous pathogens.
Figures
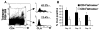

Similar articles
-
Innate immune responses to herpes simplex virus type 2 influence skin homing molecule expression by memory CD4+ lymphocytes.J Virol. 2006 Mar;80(6):2863-72. doi: 10.1128/JVI.80.6.2863-2872.2006. J Virol. 2006. PMID: 16501095 Free PMC article.
-
Homing in on the cellular immune response to HSV-2 in humans.Am J Reprod Immunol. 2005 Apr;53(4):172-81. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0897.2005.00262.x. Am J Reprod Immunol. 2005. PMID: 15760378 Free PMC article.
-
Selective Expression of CCR10 and CXCR3 by Circulating Human Herpes Simplex Virus-Specific CD8 T Cells.J Virol. 2017 Sep 12;91(19):e00810-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00810-17. Print 2017 Oct 1. J Virol. 2017. PMID: 28701399 Free PMC article.
-
The Translational Relevance of Human Circulating Memory Cutaneous Lymphocyte-Associated Antigen Positive T Cells in Inflammatory Skin Disorders.Front Immunol. 2021 Mar 23;12:652613. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.652613. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33833765 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulation of CD4+ T Helper Cell Memory Responses in the Human Skin.Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2017;173(3):121-137. doi: 10.1159/000477728. Epub 2017 Aug 9. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28787717 Review.
Cited by
-
T-cell immunity to human alphaherpesviruses.Curr Opin Virol. 2013 Aug;3(4):452-60. doi: 10.1016/j.coviro.2013.04.004. Epub 2013 May 8. Curr Opin Virol. 2013. PMID: 23664660 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Longitudinal analysis of herpes simplex virus-specific CD4+ cell clonotypes in infected tissues and blood.J Infect Dis. 2005 Jun 15;191(12):2012-21. doi: 10.1086/430389. Epub 2005 May 12. J Infect Dis. 2005. PMID: 15897986 Free PMC article.
-
Translational Mini-Review Series on Vaccines for HIV: T lymphocyte trafficking and vaccine-elicited mucosal immunity.Clin Exp Immunol. 2009 Aug;157(2):165-73. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2009.03927.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19604255 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Peripheral blood CD4 T-cell and plasmacytoid dendritic cell (pDC) reactivity to herpes simplex virus 2 and pDC number do not correlate with the clinical or virologic severity of recurrent genital herpes.J Virol. 2012 Sep;86(18):9952-63. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00829-12. Epub 2012 Jul 3. J Virol. 2012. PMID: 22761381 Free PMC article.
-
Innate immune responses to herpes simplex virus type 2 influence skin homing molecule expression by memory CD4+ lymphocytes.J Virol. 2006 Mar;80(6):2863-72. doi: 10.1128/JVI.80.6.2863-2872.2006. J Virol. 2006. PMID: 16501095 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Takahashi R, Mizukawa Y, Yamazaki Y, et al. In vitro differentiation from naive to mature E-selectin binding CD4 T cells: acquisition of skin-homing properties occurs independently of cutaneous lymphocyte antigen expression. J Immunol. 2003;171:5769–77. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

