Structural basis for discriminative regulation of gene expression by adenine- and guanine-sensing mRNAs
- PMID: 15610857
- PMCID: PMC4692365
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2004.11.018
Structural basis for discriminative regulation of gene expression by adenine- and guanine-sensing mRNAs
Abstract
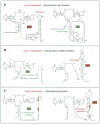
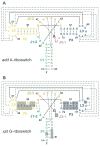
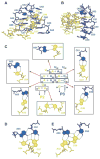
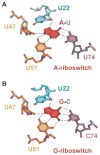
Metabolite-sensing mRNAs, or "riboswitches," specifically interact with small ligands and direct expression of the genes involved in their metabolism. Riboswitches contain sensing "aptamer" modules, capable of ligand-induced structural changes, and downstream regions, harboring expression-controlling elements. We report the crystal structures of the add A-riboswitch and xpt G-riboswitch aptamer modules that distinguish between bound adenine and guanine with exquisite specificity and modulate expression of two different sets of genes. The riboswitches form tuning fork-like architectures, in which the prongs are held in parallel through hairpin loop interactions, and the internal bubble zippers up to form the purine binding pocket. The bound purines are held by hydrogen bonding interactions involving conserved nucleotides along their entire periphery. Recognition specificity is associated with Watson-Crick pairing of the encapsulated adenine and guanine ligands with uridine and cytosine, respectively.
Figures



Comment in
-
Riboswitch structures: purine ligands replace tertiary contacts.Chem Biol. 2005 Jan;12(1):10-3. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2005.01.002. Chem Biol. 2005. PMID: 15664510 Review. No abstract available.
References
-
- Batey RT, Rambo RP, Doudna JA. Tertiary motifs in RNA structure and folding. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 1999;38:2326–2343. - PubMed
-
- Hermann T, Patel DJ. Stitching together RNA tertiary architectures. J Mol Biol. 1999;294:829–849. - PubMed
-
- Doherty EA, Doudna JA. Ribozyme structure and mechanisms. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 2001;30:457–475. - PubMed
-
- Lilley DMJ. Structure, folding and catalysis of the small nucleolytic ribozymes. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 1999;9:330–338. - PubMed
-
- Jaschke A. Artificial ribozymes and deoxyribozymes. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2001;11:321–326. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

