Increased glomerular angiotensin II binding in rats exposed to a maternal low protein diet in utero
- PMID: 15611024
- PMCID: PMC1665576
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2004.078642
Increased glomerular angiotensin II binding in rats exposed to a maternal low protein diet in utero
Abstract
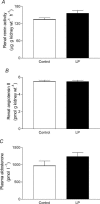
In the rat, protein restriction during pregnancy increases offspring blood pressure by 20-30 mmHg. We have shown in an earlier study that this is associated with a reduction in nephron number and increased glomerular sensitivity to angiotensin II (Ang II) in vivo. Hence, we hypothesized that exposure to a maternal low-protein diet increases glomerular Ang II AT1 receptor expression and decreases AT2 receptor expression. To test this hypothesis, pregnant Wistar rats were fed isocalorific diets containing either 18% (control) or 9% (LP) protein from conception until birth. At 4 weeks of age, the kidneys of male offspring were harvested to measure cortical AT1 and AT2 receptor expression, 125I-Ang II glomerular binding, tissue renin activity, tissue Ang II and plasma aldosterone concentrations. AT1 receptor expression was increased (62%) and AT2 expression was decreased (35%) in LP rats. Maximum 125I-Ang II (125I-Ang II) binding (Bmax) was increased in LP rats (control n = 9, 291.6 +/- 27.4 versus LP n = 7, 445.7 +/- 27.4 fmol (mg glomerular protein)(-1), P < 0.01), but affinity (KD) was not statistically different from controls (control 2.87 +/- 0.85 versus LP 0.84 +/- 0.20 pmol 125I-Ang II, P = 0.059). Renal renin activity, tissue Ang II and plasma aldosterone concentrations did not differ between control and LP rats. Increased AT1 receptor expression in LP rat kidneys is consistent with greater haemodynamic sensitivity to Ang II in vivo. This may result in an inappropriate reduction in glomerular filtration rate, salt and water retention, and an increase in blood pressure.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Renal function and angiotensin AT1 receptor expression in young rats following intrauterine exposure to a maternal low-protein diet.Clin Sci (Lond). 2003 Jun;104(6):607-14. doi: 10.1042/CS20020355. Clin Sci (Lond). 2003. PMID: 12519092
-
Maternal protein restriction reduces angiotensin II AT(1) and AT(2) receptor expression in the fetal rat kidney.Kidney Blood Press Res. 2010;33(4):251-9. doi: 10.1159/000317739. Epub 2010 Jul 2. Kidney Blood Press Res. 2010. PMID: 20606474
-
Expression of renin-angiotensin system signalling compounds in maternal protein-restricted rats: effect on renal sodium excretion and blood pressure.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2010 Feb;25(2):380-8. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfp505. Epub 2009 Sep 30. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2010. PMID: 19793932
-
Brain angiotensin receptors and binding proteins.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2008 Jun;377(4-6):283-93. doi: 10.1007/s00210-007-0238-7. Epub 2008 Jan 3. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18172611 Review.
-
The contribution of the AT1 receptor to erythropoiesis.Biochem Pharmacol. 2023 Nov;217:115805. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2023.115805. Epub 2023 Sep 14. Biochem Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37714274 Review.
Cited by
-
Sex-Specific Effect of Endothelin in the Blood Pressure Response to Acute Angiotensin II in Growth-Restricted Rats.Hypertension. 2015 Dec;66(6):1260-6. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.115.06257. Epub 2015 Oct 12. Hypertension. 2015. PMID: 26459423 Free PMC article.
-
Of Mice and Men: The Effect of Maternal Protein Restriction on Offspring's Kidney Health. Are Studies on Rodents Applicable to Chronic Kidney Disease Patients? A Narrative Review.Nutrients. 2020 May 30;12(6):1614. doi: 10.3390/nu12061614. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32486266 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of early-life diet on long-term renal health.Mol Cell Pediatr. 2020 Dec 3;7(1):17. doi: 10.1186/s40348-020-00109-1. Mol Cell Pediatr. 2020. PMID: 33269431 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fetal Undernutrition Programming, Sympathetic Nerve Activity, and Arterial Hypertension Development.Front Physiol. 2021 Nov 17;12:704819. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.704819. eCollection 2021. Front Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34867434 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rats undernourished in utero have altered Ca2+ signaling and reduced fertility in adulthood.Physiol Rep. 2015 Oct;3(10):e12587. doi: 10.14814/phy2.12587. Physiol Rep. 2015. PMID: 26508737 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aguilera G, Kapur S, Feuillan P, Sunar-Akbasak B, Bathia AJ. Developmental changes in angiotensin II receptor subtypes and AT1 receptor mRNA in rat kidney. Kidney Int. 1994;46:973–979. - PubMed
-
- Ardaillou R, Chansel D, Chatziantoniou C, Dussaule JC. Mesangial AT1 receptors: expression, signaling, and regulation. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1999;10(Suppl. 11):S40–S46. - PubMed
-
- Ashton N, Balment RJ. Sexual dimorphism in renal function and hormonal status of New Zealand genetically hypertensive rats. Acta Endocrinol. 1991;124:91–97. - PubMed
-
- Clarke HE, Coates ME, Eva JK, Ford DJ, Milner CK, O'Donoghue PN, Scott PP, Ward RJ. Dietary standards for laboratory animals: report of the Laboratory Animals Centre Diets Advisory Committee. Lab Anim. 1977;11:1–28. - PubMed
-
- Gomez RA, Lynch KR, Sturgill BC, Elwood JP, Chevalier RL, Carey RM, Peach MJ. Distribution of renin mRNA and its protein in the developing kidney. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 1989;257:F850–858. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

