Population genetics of the developmental gene optomotor-blind (omb) in Drosophila polymorpha: evidence for a role in abdominal pigmentation variation
- PMID: 15611170
- PMCID: PMC1448714
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.104.032078
Population genetics of the developmental gene optomotor-blind (omb) in Drosophila polymorpha: evidence for a role in abdominal pigmentation variation
Abstract
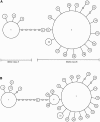
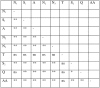
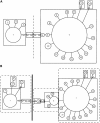
The developmental gene optomotor-blind (omb) encodes a T-box-containing transcription factor that has multiple roles in Drosophila development. Previous genetic analyses established that omb plays a key role in establishing the abdominal pigmentation pattern of Drosophila melanogaster. In this report we examine patterns of omb nucleotide variation in D. polymorpha, a species that is highly polymorphic for the phenotype of abdominal pigmentation. Haplotypes at this locus fall into two classes that are separated by six mutational steps; five of these mutational events result in amino acid changes. Two lines of evidence are consistent with a role for omb in the abdominal pigmentation polymorphism of D. polymorpha. First, we find that haplotype classes of omb are correlated with abdominal pigmentation phenotypes, as are microsatellite repeat numbers in the region. Second, tests of selection reveal that the two haplotype classes have been maintained by balancing selection. Within each class there is a significantly low amount of diversity, indicative of previous selective sweeps. An analysis including D. polymorpha's closest relatives (members of the cardini group) provides evidence for directional selection across species. Selection at this locus is expected if omb contributes to variation in abdominal pigmentation, since this trait is likely of ecological importance.
Figures
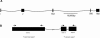


References
-
- Barnes, W. M., 1992. The fidelity of Taq polymerase catalyzing PCR is improved by an N-terminal deletion. Gene 112: 29–35. - PubMed
-
- Beachy, P., S. Helfand and D. Hogness, 1985. Segmental distribution of bithorax complex proteins during Drosophila development. Nature 313: 545–551. - PubMed
-
- Bollag, R. J., Z. Siegfried, J. A. Cebrathomas, N. Garvey, E. M. Davidson et al., 1994. An ancient family of embryonically expressed mouse genes sharing a conserved protein motif with the T-locus. Nat. Genet. 7: 383–389. - PubMed
-
- Brunner, A., R. Wolf, G. O. Pflugfelder, B. Poeck and M. Heisenberg, 1992. Mutations in the proximal region of the optomotor-blind locus of Drosophila melanogaster reveal a gradient of neuroanatomical and behavioral phenotypes. J. Neurogenet. 8: 43–50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

