Risk factors and neuropsychological recovery in clients with alcohol use disorders who were exposed to different treatments
- PMID: 15612853
- PMCID: PMC2980291
- DOI: 10.1037/0022-006X.72.6.1073
Risk factors and neuropsychological recovery in clients with alcohol use disorders who were exposed to different treatments
Abstract
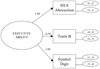
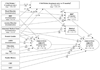
Risk covariates of neuropsychological ability (NA) at treatment entry and neuropsychological recovery (NR) across 15 months were examined and replicated in 2 samples (Ns = 952 and 774) from Project MATCH, a multisite study of alcoholism treatments. NA at treatment entry was associated with age, education, and other covariates. Statistically significant mean increases in NA over time had small effect sizes, suggesting limited clinical significance of NR in the samples as a whole. However, initial NA and a combination of risk factors in direct and mediated pathways predicted a large proportion of individual differences in NR. Statistically significant but modest differential treatment effects on NR suggest that addiction treatments may need to be modified or developed to facilitate this important aspect of recovery.
Copyright 2004 APA.
Figures
References
-
- Allen DN, Goldstein G, Seaton BE. Cognitive rehabilitation of chronic alcohol abusers. Neuropsychology Review. 1997;7(1):21–39. - PubMed
-
- Allison PD. Missing data. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications; 2002.
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. 3rd ed. Washington, DC: Author; 1987. rev.
-
- Bates ME. Stability of neuropsychological assessments early in alcoholism treatment. Journal of Studies on Alcohol. 1997;58:617–621. - PubMed
-
- Bates M, Convit A. Neuropsychology and neuroimaging of alcohol and illicit drug abuse. In: Calev A, editor. The Assessment of Neuropsychological Functions in Psychiatric Disorders. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Press; 1999. pp. 373–445.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

