Randomised controlled trial of conservative management of postnatal urinary and faecal incontinence: six year follow up
- PMID: 15615766
- PMCID: PMC548727
- DOI: 10.1136/bmj.38320.613461.82
Randomised controlled trial of conservative management of postnatal urinary and faecal incontinence: six year follow up
Abstract
Objective: To determine the long term effects of a conservative nurse-led intervention for postnatal urinary incontinence.
Design: Randomised controlled trial.
Setting: Community based intervention in three centres in the United Kingdom and New Zealand.
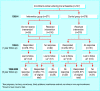
Participants: 747 women with urinary incontinence at three months after childbirth, of whom 516 were followed up again at 6 years (69%).
Intervention: Active conservative treatment (pelvic floor muscle training and bladder training) at five, seven, and nine months after delivery or standard care.
Main outcome measures: Urinary and faecal incontinence, performance of pelvic floor muscle training.
Results: Of 2632 women with urinary incontinence, 747 participated in the original trial. The significant improvements relative to controls in urinary (60% v 69%) and faecal (4% v 11%) incontinence at one year were not found at six year follow up (76% v 79% (95% confidence interval for difference in means -10.2% to 4.1%) for urinary incontinence, 12% v 13% (-6.4% to 5.1%) for faecal incontinence) irrespective of subsequent obstetric events. In the short term the intervention had motivated more women to perform pelvic floor muscle training (83% v 55%) but this fell to 50% in both groups in the long term. Both urinary and faecal incontinence increased in prevalence in both groups during the study period.
Conclusions: The moderate short term benefits of a brief nurse-led conservative treatment of postnatal urinary incontinence may not persist, even among women with no further deliveries. About three quarters of women with urinary incontinence three months after childbirth still have this six years later.
Figures
References
-
- Wilson PD, Herbison RM, Herbison GP. Obstetric practice and the prevalence of urinary incontinence three months after delivery. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1996;103: 154-61. - PubMed
-
- MacArthur C, Bick DE, Keighley MR. Faecal incontinence after childbirth. Br J Obstet Gynaecol 1997;104: 46-50. - PubMed
-
- Hay-Smith EJC, Bo K, Berghmans LCM, Hendriks HJM, de Bie RA, van Waalwijk van Doorn ESC. Pelvic floor muscle training for urinary incontinence in women. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2001;(1): CD001407. - PubMed
-
- Wilson PD, Herbison GP. A randomized controlled trial of pelvic floor muscle exercises to treat postnatal urinary incontinence. Int Urogynecol J 1998;9: 257-64. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical