A specific alpha5beta1-integrin conformation promotes directional integrin translocation and fibronectin matrix formation
- PMID: 15615773
- PMCID: PMC3329624
- DOI: 10.1242/jcs.01623
A specific alpha5beta1-integrin conformation promotes directional integrin translocation and fibronectin matrix formation
Abstract
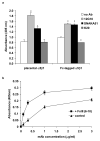
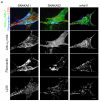
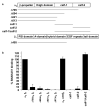
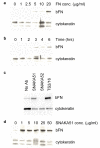
Integrin adhesion receptors are structurally dynamic proteins that adopt a number of functionally relevant conformations. We have produced a conformation-dependent anti-alpha5 monoclonal antibody (SNAKA51) that converts alpha5beta1 integrin into a ligand-competent form and promotes fibronectin binding. In adherent fibroblasts, SNAKA51 preferentially bound to integrins in fibrillar adhesions. Clustering of integrins expressing this activation epitope induced directional translocation of alpha5beta1, mimicking fibrillar adhesion formation. Priming of alpha5beta1 integrin by SNAKA51 increased the accumulation of detergent-resistant fibronectin in the extracellular matrix, thus identifying an integrin conformation that promotes matrix assembly. The SNAKA51 epitope was mapped to the calf-1/calf-2 domains. We propose that the action of the antibody causes the legs of the integrin to change conformation and thereby primes the integrin to bind ligand. These findings identify SNAKA51 as the first anti-integrin antibody to selectively recognize a subset of adhesion contacts, and they identify an integrin conformation associated with integrin translocation and fibronectin matrix formation.
Figures
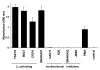


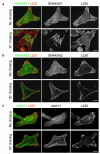

Inactive integrin is diffusely located on the cell surface.
α5β1 located in focal adhesions expresses epitopes reporting a primed β1 conformation (e.g. 9EG7). These integrins may or may not be fully bound by ligand.
Integrin located at the distal edge of focal adhesions has additional SNAKA51 epitope expression. Clustering of this integrin promotes translocation.
Ligated-clustered integrin translocates out of focal adhesions along the actin cytoskeleton, stretching extracellular fibronectin fibrils and driving fibrillogenesis.
References
-
- Bazzoni G, Shih DT, Buck CA, Hemler ME. Monoclonal antibody 9EG7 defines a novel beta 1 integrin epitope induced by soluble ligand and manganese, but inhibited by calcium. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:25570–7. - PubMed
-
- Beglova N, Blacklow SC, Takagi J, Springer TA. Cysteine-rich module structure reveals a fulcrum for integrin rearrangement upon activation. Nat Struct Biol. 2002;9:282–7. - PubMed
-
- Calderwood DA. Integrin activation. J Cell Sci. 2004;117:657–66. - PubMed
-
- Calvete JJ, Arias J, Alvarez MV, Lopez MM, Henschen A, Gonzalez-Rodriguez J. Further studies on the topography of human platelet glycoprotein IIb. Localization of monoclonal antibody epitopes and the putative glycoprotein IIa- and fibrinogen-binding regions. Biochem J. 1991;273(Pt 3):767–75. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

