Advances in surface-enhanced fluorescence
- PMID: 15617385
- PMCID: PMC2763917
- DOI: 10.1023/b:jofl.0000031824.48401.5c
Advances in surface-enhanced fluorescence
Abstract
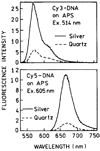
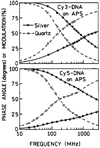
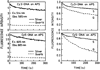
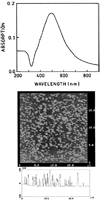
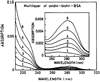
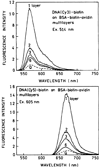
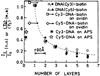
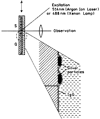
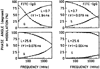
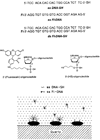
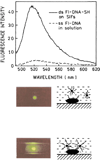
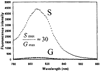
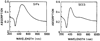
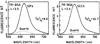
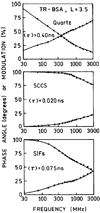
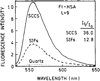
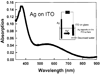
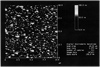
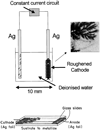
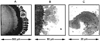
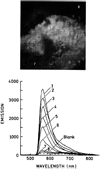
We report recent achievements in metal-enhanced fluorescence from our laboratory. Several fluorophore systems have been studied on metal particle-coated surfaces and in colloid suspensions. In particular, we describe a distance dependent enhancement on silver island films (SIFs), release of self-quenching of fluorescence near silver particles, and the applications of fluorescence enhancement near metalized surfaces to bioassays. We discuss a number of methods for various shaped silver particle deposition on surfaces.
Figures





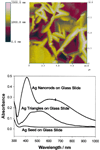
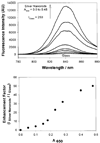
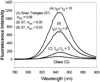
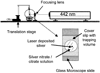


References
-
- Drexhage KH. In: Progress in Optics. Wolfe E, editor. Amsterdam: North-Holland; 1974. pp. 161–323.
-
- Weitz DA, Garoff S, Hansen CD, Gramila TJ. Fluorescent lifetimes of molecules on silver-island films. Opt. Lett. 1982;7(2):89–91. - PubMed
-
- Aussenegg FR, Leitner A, Lippitsch ME, Reinish H, Reigler M. Novel aspects of fluorescence lifetime for molecules positioned close to metal surfaces. Surf. Sci. 1987;139:935–945.
-
- Leitner A, Lippitsch ME, Draxler S, Reigler M, Aussenegg FR. Fluorescence properties of dyes absorbed to silver islands, investigated by picosecond techniques. Appl. Phys. B. 1985;36:106–109.
-
- Gersten J, Nitzan A. Spectroscopic properties of molecules interacting with small dielectric particles. J. Chem. Phys. 1981;75(3):1139–1152.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
