Nitrosative stress induces DNA strand breaks but not caspase mediated apoptosis in a lung cancer cell line
- PMID: 15617570
- PMCID: PMC544845
- DOI: 10.1186/1477-3163-3-16
Nitrosative stress induces DNA strand breaks but not caspase mediated apoptosis in a lung cancer cell line
Abstract
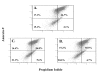
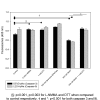
BACKGROUND: Key steps crucial to the process of tumor progression are genomic instability and escape from apoptosis. Nitric oxide and its interrelated reactive intermediates (collectively denoted as NOX) have been implicated in DNA damage and mutational events leading to cancer development, while also being implicated in the inhibition of apoptosis through S-nitrosation of key apoptotic enzymes. The purpose of this study was to explore the interrelationship between NOX-mediated DNA strand breaks (DSBs) and apoptosis in cultured tumor cell lines. METHODS: Two well-characterized cell lines were exposed to increasing concentrations of exogenous NOX via donor compounds. Production of NOX was quantified by the Greiss reaction and spectrophotometery, and confirmed by nitrotyrosine immunostaining. DSBs were measured by the alkaline single-cell gel electrophoresis assay (the COMET assay), and correlated with cell viability by the MTT assay. Apoptosis was analyzed both by TUNEL staining and Annexin V/propidium iodine FACS. Finally, caspase enzymatic activity was measured using an in-vitro fluorogenic caspase assay. RESULTS: Increases in DNA strand breaks in our tumor cells, but not in control fibroblasts, correlated with the concentration as well as rate of release of exogenously administered NOX. This increase in DSBs did not correlate with an increase in cell death or apoptosis in our tumor cell line. Finally, this lack of apoptosis was found to correlate with inhibition of caspase activity upon exposure to thiol- but not NONOate-based NOX donor compounds. CONCLUSIONS: Genotoxicity appears to be highly interrelated with both the concentration and kinetic delivery of NOX. Moreover, alterations in cell apoptosis can be seen as a consequence of the explicit mechanisms of NOX delivery. These findings lend credence to the hypothesis that NOX may play an important role in tumor progression, and underscores potential pitfalls which should be considered when developing NOX-based chemotherapeutic agents.
Figures

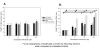

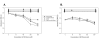
References
-
- Bentz BG, Haines GK, Hanson DG, Radosevich JA. Endothelial constitutive nitric oxide synthase (ecNOS) localization in normal and neoplastic salivary tissue. Head Neck. 1998;20:304–309. - PubMed
-
- Bentz BG, Barnes MN, Haines GK, Lurain JR, Hanson DG, Radosevich JA. Cytoplasmic localization of endothelial constitutive nitric oxide synthase in endometrial carcinomas. Tumour Biol. 1997;18:290–300. - PubMed
-
- Bentz BG, Haines GK, Lingen MW, Pelzer HJ, Hanson DG, Radosevich JA. Nitric oxide synthase type 3 is increased in squamous hyperplasia, dysplasia, and squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1999;108:781–787. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

