Differences in patterns of infection and inflammation for corticosteroid treatment and chemotherapy in experimental invasive pulmonary aspergillosis
- PMID: 15618189
- PMCID: PMC538925
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.73.1.494-503.2005
Differences in patterns of infection and inflammation for corticosteroid treatment and chemotherapy in experimental invasive pulmonary aspergillosis
Abstract
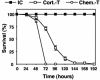
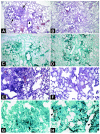
Aspergillus fumigatus causes invasive pulmonary aspergillosis (IPA). This disease is one of the most life-threatening opportunistic infections in immunocompromised patients. The type of immunosuppressive regimen under which IPA occurs has rarely been investigated. In this study, we evaluated various parameters of the innate immune response during the progression of murine IPA induced by the intratracheal administration of A. fumigatus conidia as a function of two immunosuppressive treatments: a corticosteroid and a chemotherapeutic agent. We compared host responses various times after infection in terms of survival, pulmonary production of pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines, cellular trafficking in the airways, lung injury, respiratory distress, and fungal development. We found that IPA pathogenesis involved predominantly fungal development in mice treated by chemotherapy and an adverse host response in mice treated with a corticosteroid. These previously unrecognized differences should be taken into account in evaluations of the pathogenesis of IPA in animal models.
Figures
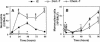

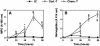



References
-
- Balloy, V., J. M. Sallenave, B. Crestani, M. Dehoux, and M. Chignard. 2003. Neutrophil DNA contributes to the antielastase barrier during acute lung inflammation. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 28:746-753. - PubMed
-
- Becker, M. J., S. de Marie, M. H. Fens, H. A. Verbrugh, and I. A. Bakker-Woudenberg. 2003. Effect of amphotericin B treatment on kinetics of cytokines and parameters of fungal load in neutropenic rats with invasive pulmonary aspergillosis. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 52:428-434. - PubMed
-
- Berenguer, J., M. C. Allende, J. W. Lee, K. Garrett, C. Lyman, N. M. Ali, J. Bacher, P. A. Pizzo, and T. J. Walsh. 1995. Pathogenesis of pulmonary aspergillosis. Granulocytopenia versus cyclosporin and methylprednisolone-induced immunosuppression. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 152:1079-1086. - PubMed
-
- Brieland, J. K., C. Jackson, F. Menzel, D. Loebenberg, A. Cacciapuoti, J. Halpern, S. Hurst, T. Muchamuel, R. Debets, R. Kastelein, T. Churakova, J. Abram, R. Hare, and A. O'Garra. 2001. Cytokine networking in lungs of immunocompetent mice in response to inhaled Aspergillus fumigatus. Infect. Immun. 69:1554-1560. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cenci, E., A. Mencacci, C. F. d'Ostiani, G. Del Sero, P. Mosci, C. Montagnoli, A. Bacci, and L. Romani. 1998. Cytokine- and T helper-dependent lung mucosal immunity in mice with invasive pulmonary aspergillosis. J. Infect. Dis. 178:1750-1760. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

