Chlamydia pneumoniae enhances cytokine-stimulated human monocyte matrix metalloproteinases through a prostaglandin E2-dependent mechanism
- PMID: 15618206
- PMCID: PMC538927
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.73.1.632-634.2005
Chlamydia pneumoniae enhances cytokine-stimulated human monocyte matrix metalloproteinases through a prostaglandin E2-dependent mechanism
Abstract
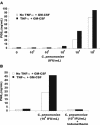
Exposure of human monocytes to Chlamydia pneumoniae resulted in a significant enhancement of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) 1 and 9 production following stimulation with tumor necrosis factor alpha and granulocyte monocyte-colony stimulating factor. The effect of C. pneumoniae on monocyte MMPs was mediated through the induction of prostaglandin E(2). These findings may have implications for atherosclerotic plaque rupture.
Figures


References
-
- Danesh, J., P. Whincup, S. Lewington, M. Walker, L. Lennon, A. Thomson, Y. K. Wong, X. Zhou, and M. Ward. 2002. Chlamydia pneumoniae IgA titres and coronary heart disease; prospective study and meta-analysis. Eur. Heart J. 23:371-375. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

