Sustained Hedgehog signaling is required for basal cell carcinoma proliferation and survival: conditional skin tumorigenesis recapitulates the hair growth cycle
- PMID: 15625189
- PMCID: PMC545881
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1258705
Sustained Hedgehog signaling is required for basal cell carcinoma proliferation and survival: conditional skin tumorigenesis recapitulates the hair growth cycle
Abstract
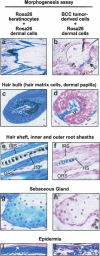
Temporally and spatially constrained Hedgehog (Hh) signaling regulates cyclic growth of hair follicle epithelium while constitutive Hh signaling drives the development of basal cell carcinomas (BCCs), the most common cancers in humans. Using mice engineered to conditionally express the Hh effector Gli2, we show that continued Hh signaling is required for growth of established BCCs. Transgene inactivation led to BCC regression accompanied by reduced tumor cell proliferation and increased apoptosis, leaving behind a small subset of nonproliferative cells that could form tumors upon transgene reactivation. Nearly all BCCs arose from hair follicles, which harbor cutaneous epithelial stem cells, and reconstitution of regressing tumor cells with an inductive mesenchyme led to multilineage differentiation and hair follicle formation. Our data reveal that continued Hh signaling is required for proliferation and survival of established BCCs, provide compelling support for the concept that these tumors represent an aberrant form of follicle organogenesis, and uncover potential limitations to treating BCCs using Hh pathway inhibitors.
Figures



References
-
- Aszterbaum M., Epstein, J., Oro, A., Douglas, V., LeBoit, P.E., Scott, M.P., and Epstein Jr., E.H. 1999. Ultraviolet and ionizing radiation enhance the growth of BCCs and trichoblastomas in patched heterozygous knockout mice. Nat. Med. 5: 1285–1291. - PubMed
-
- Bai C.B., Auerbach, W., Lee, J.S., Stephen, D., and Joyner, A.L. 2002. Gli2, but not Gli1, is required for initial Shh signaling and ectopic activation of the Shh pathway. Development 129: 4753–4761. - PubMed
-
- Bale A.E. and Yu, K.P. 2001. The hedgehog pathway and basal cell carcinomas. Hum. Mol. Genet. 10: 757–762. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
