Comparative genomics of Staphylococcus aureus musculoskeletal isolates
- PMID: 15629929
- PMCID: PMC543526
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.187.2.576-592.2005
Comparative genomics of Staphylococcus aureus musculoskeletal isolates
Abstract
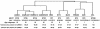
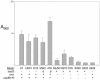
Much of the research aimed at defining the pathogenesis of Staphylococcus aureus has been done with a limited number of strains, most notably the 8325-4 derivative RN6390. Several lines of evidence indicate that this strain is unique by comparison to clinical isolates of S. aureus. Based on this, we have focused our efforts on two clinical isolates (UAMS-1 and UAMS-601), both of which are hypervirulent in our animal models of musculoskeletal infection. In this study, we used comparative genomic hybridization to assess the genome content of these two isolates relative to RN6390 and each of seven sequenced S. aureus isolates. Our comparisons were done by using an amplicon-based microarray from the Pathogen Functional Genomics Resource Center and an Affymetrix GeneChip that collectively represent the genomes of all seven sequenced strains. Our results confirmed that UAMS-1 and UAMS-601 share specific attributes that distinguish them from RN6390. Potentially important differences included the presence of cna and the absence of isaB, sarT, sarU, and sasG in the UAMS isolates. Among the sequenced strains, the UAMS isolates were most closely related to the dominant European clone EMRSA-16. In contrast, RN6390, NCTC 8325, and COL formed a distinct cluster that, by comparison to the other four sequenced strains (Mu50, N315, MW2, and SANGER-476), was the most distantly related to the UAMS isolates and EMRSA-16.
Figures

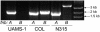
Similar articles
-
Transcriptional profiling of a Staphylococcus aureus clinical isolate and its isogenic agr and sarA mutants reveals global differences in comparison to the laboratory strain RN6390.Microbiology (Reading). 2006 Oct;152(Pt 10):3075-3090. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.29033-0. Microbiology (Reading). 2006. PMID: 17005987
-
Strain-dependent differences in the regulatory roles of sarA and agr in Staphylococcus aureus.Infect Immun. 2002 Feb;70(2):470-80. doi: 10.1128/IAI.70.2.470-480.2002. Infect Immun. 2002. PMID: 11796572 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of the sarA family of genes in different strains of Staphylococcus aureus.Microbiology (Reading). 2009 Jul;155(Pt 7):2342-2352. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.027417-0. Epub 2009 Apr 23. Microbiology (Reading). 2009. PMID: 19389785 Free PMC article.
-
Genomics of Natural Populations of Staphylococcus aureus.Annu Rev Microbiol. 2016 Sep 8;70:459-78. doi: 10.1146/annurev-micro-102215-095547. Epub 2016 Jul 29. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27482738 Review.
-
Molecular pathogenesis of staphylcoccal osteomyelitis.Poult Sci. 2000 Jul;79(7):1042-9. doi: 10.1093/ps/79.7.1042. Poult Sci. 2000. PMID: 10901208 Review.
Cited by
-
Changes in the Staphylococcus aureus transcriptome during early adaptation to the lung.PLoS One. 2012;7(8):e41329. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0041329. Epub 2012 Aug 2. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22876285 Free PMC article.
-
Presence and mRNA Expression of the sar Family Genes in Clinical and Non-clinical (Healthy Conjunctiva and Healthy Skin) Isolates of Staphylococcus epidermidis.Indian J Microbiol. 2024 Sep;64(3):1301-1309. doi: 10.1007/s12088-024-01339-x. Epub 2024 Jul 2. Indian J Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39282185
-
Cinnamonitrile Adjuvants Restore Susceptibility to β-Lactams against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus.ACS Med Chem Lett. 2019 Jul 1;10(8):1148-1153. doi: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.9b00169. eCollection 2019 Aug 8. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2019. PMID: 31413798 Free PMC article.
-
Influenza virus primes mice for pneumonia from Staphylococcus aureus.J Infect Dis. 2011 Mar 15;203(6):880-8. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiq113. Epub 2011 Jan 28. J Infect Dis. 2011. PMID: 21278211 Free PMC article.
-
CodY-mediated regulation of the Staphylococcus aureus Agr system integrates nutritional and population density signals.J Bacteriol. 2014 Mar;196(6):1184-96. doi: 10.1128/JB.00128-13. Epub 2014 Jan 3. J Bacteriol. 2014. PMID: 24391052 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arvidson, S., and K. Tegmark. 2001. Regulation of virulence determinants in Staphylococcus aureus. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 291:159-170. - PubMed
-
- Baba, T., F. Takeuchi, M. Kuroda, H. Yuzawa, K. Aoki, A. Oguchi, Y. Nagai, N. Iwama, K. Asano, T. Naimi, H. Kuroda, L. Cui, K. Yamamoto, and K. Hiramatsu. 2002. Genome and virulence determinants of high virulence community-acquired MRSA. Lancet 359:1819-1827. - PubMed
-
- Balaban, N., T. Goldkorn, Y. Gov, M. Hirshberg, N. Koyfman, H. R. Matthews, R. T. Nhan, B. Singh, and O. Uziel. 2001. Regulation of Staphylococcus aureus pathogenesis via target of RNAIII-activating protein (TRAP). J. Biol. Chem. 276:2658-2667. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

