Cobalamin-independent methionine synthase (MetE): a face-to-face double barrel that evolved by gene duplication
- PMID: 15630480
- PMCID: PMC539065
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0030031
Cobalamin-independent methionine synthase (MetE): a face-to-face double barrel that evolved by gene duplication
Abstract
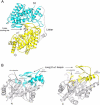
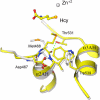
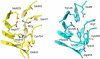
Cobalamin-independent methionine synthase (MetE) catalyzes the transfer of a methyl group from methyltetrahydrofolate to L-homocysteine (Hcy) without using an intermediate methyl carrier. Although MetE displays no detectable sequence homology with cobalamin-dependent methionine synthase (MetH), both enzymes require zinc for activation and binding of Hcy. Crystallographic analyses of MetE from T. maritima reveal an unusual dual-barrel structure in which the active site lies between the tops of the two (betaalpha)(8) barrels. The fold of the N-terminal barrel confirms that it has evolved from the C-terminal polypeptide by gene duplication; comparisons of the barrels provide an intriguing example of homologous domain evolution in which binding sites are obliterated. The C-terminal barrel incorporates the zinc ion that binds and activates Hcy. The zinc-binding site in MetE is distinguished from the (Cys)(3)Zn site in the related enzymes, MetH and betaine-homocysteine methyltransferase, by its position in the barrel and by the metal ligands, which are histidine, cysteine, glutamate, and cysteine in the resting form of MetE. Hcy associates at the face of the metal opposite glutamate, which moves away from the zinc in the binary E.Hcy complex. The folate substrate is not intimately associated with the N-terminal barrel; instead, elements from both barrels contribute binding determinants in a binary complex in which the folate substrate is incorrectly oriented for methyl transfer. Atypical locations of the Hcy and folate sites in the C-terminal barrel presumably permit direct interaction of the substrates in a ternary complex. Structures of the binary substrate complexes imply that rearrangement of folate, perhaps accompanied by domain rearrangement, must occur before formation of a ternary complex that is competent for methyl transfer.
Figures





References
-
- Ludwig ML, Matthews RG. Structure-based perspectives on B12-dependent enzymes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1997;66:269–313. - PubMed
-
- Peariso K, Zhou ZS, Smith AE, Matthews RG, Penner-Hahn JE. Characterization of the zinc sites in cobalamin-independent and cobalamin-dependent methionine synthase using zinc and selenium x-ray absorption spectroscopy. Biochemistry. 2001;40:987–993. - PubMed
-
- Matthews RG, Smith AE, Zhou ZS, Taurog RE, Bandarian V, et al. Cobalamin-dependent and cobalamin-independent methionine synthases: Are there two solutions to the same chemical problem? Helvetica Chimica Acta. 2003;86:3939–3954.
-
- Hightower KE, Fierke CA. Zinc-catalyzed sulfur alkylation: Insights from protein farnesyltransferase. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 1999;3:176–181. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

